Chapter: Cryptography and Network Security
Firewalls: design principles, characteristics, Limitations, Types
FIREWALLS
1. Firewall design principles
Internet
connectivity is no longer an option for most organizations. However, while
internet access provides benefits to the organization, it enables the outside
world to reach and interact with local network assets. This creates the threat
to the organization. While it is possible to equip each workstation and server
on the premises network with strong security features, such as intrusion
protection, this is not a practical approach. The alternative, increasingly
accepted, is the firewall.
The
firewall is inserted between the premise network and internet to establish a
controlled link and to erect an outer security wall or perimeter. The aim of
this perimeter is to protect the premises network from internet based attacks
and to provide a single choke point where security and audit can be imposed.
The firewall can be a single computer system or a set of two or more systems
that cooperate to perform the firewall function.
2. Firewall characteristics:
·
All traffic from inside to outside, and vice versa,
must pass through the firewall. This is achieved by physically blocking all
access to the local network except via the firewall.
·
Various configurations are possible.
·
·
Only authorized traffic, as defined by the local
security policy, will be allowed to pass.
·
Various types of firewalls are used, which
implement various types of security policies.
·
·
The firewall itself is immune to penetration. This
implies that use of a trusted system with a secure operating system. This
implies that use of a trusted system with a secure operating system.
Four
techniques that firewall use to control access and enforce the site‟s security
policy is as follows:
1. Service
control – determines the type of internet services that can be accessed,
inbound or outbound. The firewall may filter traffic on this basis of IP
address and TCP port number; may provide proxy software that receives and
interprets each service request before passing it on; or may host the server
software itself, such as web or mail service.
2. Direction
control – determines the direction in which particular service request may be initiated
and allowed to flow through the firewall.
3. User
control – controls access to a service according to which user is attempting to
access it.
4. Behavior
control – controls how particular services are used.
Capabilities of firewall
A
firewall defines a single choke point that keeps unauthorized users out of the
protected network, prohibits potentially vulnerable services from entering or
leaving the network, and provides protection from various kinds of IP spoofing
and routing attacks.
A
firewall provides a location for monitoring security related events. Audits and
alarms can be implemented on the firewall system.
A
firewall is a convenient platform for several internet functions that are not
security related.
A
firewall can serve as the platform for IPsec.
3. Limitations of firewall
·
The firewall cannot protect against attacks that
bypass the firewall. Internal systems may have dial-out capability to connect
to an ISP. An internal LAN may support a modem pool that provides dial-in
capability for traveling employees and telecommuters.
·
The firewall does not protect against internal
threats. The firewall does not protect against internal threats, such as a
disgruntled employee or an employee who unwittingly cooperates with an external
attacker.
·
The firewall cannot protect against the transfer of
virus-infected programs or files. Because of the variety of operating systems
and applications supported inside the perimeter, it would be impractical and
perhaps impossible for the firewall to scan all incoming files, e-mail, and
messages for viruses.
4 Types of firewalls
There are
3 common types of firewalls.
·
Packet filters
·
·
Application-level gateways
·
·
Circuit-level gateways
Packet filtering router
A packet
filtering router applies a set of rules to each incoming IP packet and then
forwards or discards the packet. The router is typically configured to filter
packets going in both directions. Filtering rules are based on the information
contained in a network packet:
·
Source IP address – IP address of the system that
originated the IP packet. Destination IP address – IP address of the
system, the IP is trying to reach. Source and destination transport level address
– transport level port number. IP protocol field – defines the transport
protocol.
·
Interface – for a router with three or more ports,
which interface of the router the packet come from or which interface of the
router the packet is destined for.
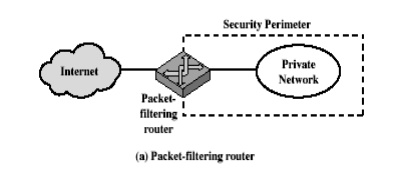
The
packet filter is typically set up as a list of rules based on matches to fields
in the IP or TCP header. If there is a match to one of the rules, that rule is
invoked to determine whether to forward or discard the packet. If there is no
match to any rule, then a default action is taken.
Two
default policies are possible:
· Default = discard: That which is not expressly permitted is prohibited.
· Default = forward: That which is not expressly prohibited is permitted.
The
default discard policy is the more conservative. Initially everything is
blocked, and services must be added on a case-by-case basis. This policy is
more visible to users, who are most likely to see the firewall as a hindrance.
The default forward policy increases ease of use for end users but provides
reduced security.
5. Advantages of packet filter
router
· Simple
· Transparent to users
Very fast
Weakness of packet filter firewalls
· Because
packet filter firewalls do not examine upper-layer data, they cannot prevent attacks
that employ application specific vulnerabilities or functions.
·
Because of the limited information available to the
firewall, the logging functionality present in packet filter firewall is
limited.
·
It does not support advanced user authentication
schemes.
·
They are generally vulnerable to attacks such as
layer address spoofing.
Some of
the attacks that can be made on packet filtering routers and the appropriate
counter measures are the following:
· IP
address spoofing – the intruders transmit packets from the outside with a
source IP address field containing an address of an internal host.
Countermeasure: to discard packet with an inside source address if
the packet arrives on an external interface.
·
Source routing attacks – the source station
specifies the route that a packet should take as it
crosses the internet; i.e., it will bypass the firewall.
·
Tiny fragment attacks – the intruder create
extremely small fragments and force the TCP header information into a separate
packet fragment. The attacker hopes that only the first fragment is examined
and the remaining fragments are passed through.
Countermeasure: to
discard all packets where the protocol type is TCP and the IP fragment offset
is equal to 1.
6. Application level gateway
An
Application level gateway, also called a proxy server, acts as a relay of
application level traffic. The user contacts the gateway using a TCP/IP
application, such as Telnet or FTP, and the gateway asks the user for the name
of the remote host to be accessed. When the user responds and provides a valid
user ID and authentication information, the gateway contacts the application on
the remote host and relays TCP segments containing the application data between
the two endpoints.
Application
level gateways tend to be more secure than packet filters. It is easy to log
and audit all incoming traffic at the application level. A prime disadvantage
is the additional processing overhead on each connection.
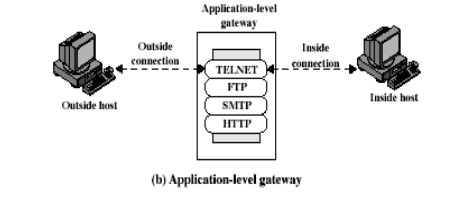
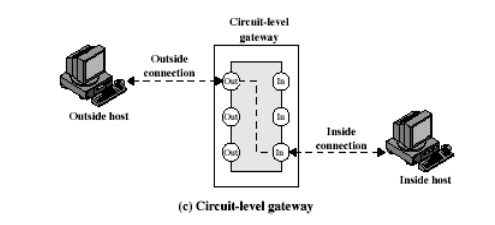
7 Circuit level gateway
Circuit
level gateway can be a stand-alone system or it can be a specified function
performed by an application level gateway for certain applications. A Circuit
level gateway does not permit an end-to-end TCP connection; rather, the gateway
sets up two TCP connections, one between itself and a TCP user on an inner host
and one between itself and a TCP user on an outer host. Once the two
connections are established, the gateway typically relays TCP segments from one
connection to the other without examining the contents. The security function
consists of determining which connections will be allowed.
A typical
use of Circuit level gateways is a situation in which the system administrator
trusts the internal users. The gateway can be configured to support application
level or proxy service on inbound connections and circuit level functions for
outbound connections.
Basiton host
It is a
system identified by the firewall administrator as a critical strong point in
the network‟s security. The Bastion host serves as a platform for an
application level and circuit level gateway.
Common
characteristics of a Basiton host are as follows:
·
The Bastion host hardware platform executes a
secure version of its operating system, making it a trusted system.
·
Only the services that the network administrator
considers essential are installed on the Bastion host.
·
It may require additional authentication before a
user is allowed access to the proxy services.
·
Each proxy is configured to support only a subset
of standard application‟s command set.
·
Each proxy is configured to allow access only to
specific host systems.
·
Each proxy maintains detailed audit information by
logging all traffic, each connection
·
and the duration of each connection.
·
Each proxy is independent of other proxies on the
Bastion host.
·
A proxy generally performs no disk access other
than to read its initial configuration file.
·
Each proxy runs on a non privileged user in a
private and secured directory on the Bastion host.
Related Topics