Chapter:
Firewall configurations
Firewall configurations
There are
3 common firewall configurations.
1. Screened host firewall, single-homed basiton configuration
2. Screened host firewall, dual homed basiton configuration
3. Screened subnet firewall configuration
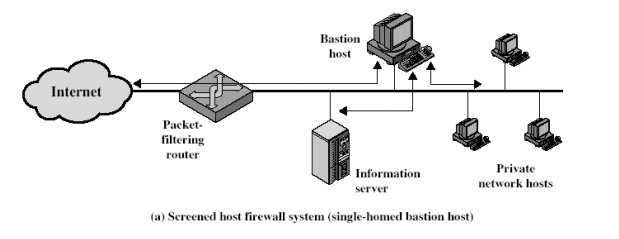
1. Screened host firewall,
single-homed basiton configuration
In this
configuration, the firewall consists of two systems: a packet filtering router
and a bastion host. Typically, the router is configured so that
o
For traffic from the internet, only IP packets
destined for the basiton host are allowed in.
o
For traffic from the internal network, only IP
packets from the basiton host are allowed out.
The
basiton host performs authentication and proxy functions. This configuration
has greater security than simply a packet filtering router or an application
level gateway alone, for two reasons:
·
This configuration implements both packet level and
application level filtering, allowing for considerable flexibility in defining
security policy.
·
An intruder must generally penetrate two separate
systems before the security of the internal network is compromised.
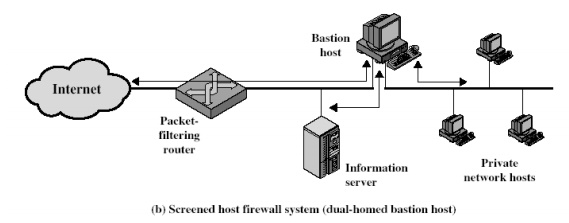
2. Screened host firewall, dual
homed basiton configuration
In the
previous configuration, if the packet filtering router is compromised, traffic
could flow directly through the router between the internet and the other hosts
on the private network. This configuration physically prevents such a security
break.
3. Screened subnet firewall
configuration
In this
configuration, two packet filtering routers are used, one between the basiton
host and internet and one between the basiton host and the internal network.
This configuration creates an isolated subnetwork, which may consist of simply
the basiton host but may also include one or more information servers and
modems for dial-in capability. Typically both the internet and the internal
network have access to hosts on the screened subnet, but traffic across the
screened subnet is blocked. This configuration offers several advantages:
· There are
now three levels of defense to thwart intruders.
· The
outside router advertises only the existence of the screened subnet to the
internet; therefore the internal network is invisible to the internet.
·
Similarly, the inside router advertises only the
existence of the screened subnet to the internal network; therefore the systems
on the internal network cannot construct direct routes to the internet.