Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Electronegativity
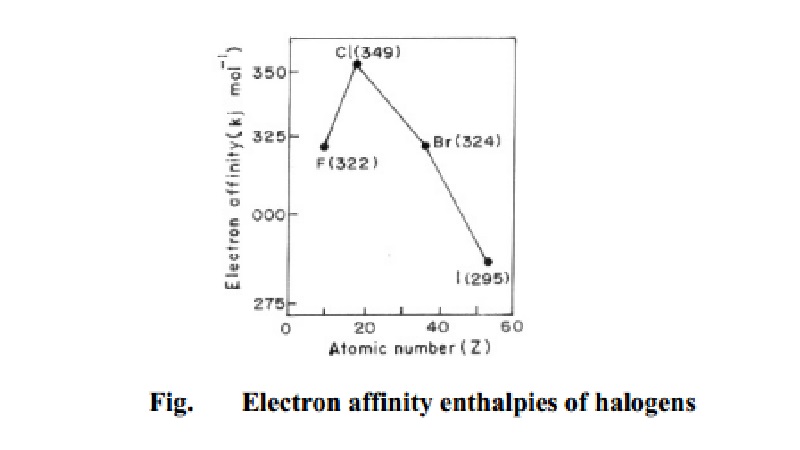
Electronegativity
Electronegativity
may be defined as the tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract towards
itself the shared pair of electrons. The main factors, which the electronegativity
depends, are effective nuclear charge and atomic radius. Greater the effective
nuclear charge greater is the electronegativity. Smaller the atomic radius
greater is the electronegativity.
In a period electronegativity increases in
moving from left to right. This is due to the reason that the nuclear charge
increases whereas atomic radius decreases as we move from left to right in a
period. Halogens have the highest value of electronegativity in their
respective periods.
In a group electronegativity decreases on moving
down the group. This is due to the effect of the increased atomic radius. Among
halogens fluorine has the highest electronegativity. In fact fluorine is the
most electronegative element and is given a value of 4.0 (Pauling's scale)
whereas cesium is the least electronegative element (E.N. = 0.7) because of its
largest size and maximum screening effect. In other words, cesium is the most
electropositive element and hence is the most metallic element in the periodic
table.
The main differences between Electron gain
enthalpy (electro affinity) and electronegativity are given below :
Electron
gain Enthalpy
1.
It is the tendency of an isolated gaseous atom attract an electron.
2.
It is measured in electron volts/atom or kcal/mole kj/mole.
3.
It is the property of an isolated atom.
4.
An atom has
an absolute value of electron gain enthalpy.
5.
It does not change regularly
6.
in a period or group.
Electronegativity
1.
It is the tendency of an atom in a molecule to
attract the shared pair of
electrons.
2.
It is a number and has no units.
3.
It is property of a bonded atom.
4.
An
atom has a
relative value of electronegativity depending upon
its bonding state.
5.
For example, sp-hybridized carbon is more electronegative than sp2-hybridized
carbon which, in turn, is more
electronegative than sp3- hybridized carbon.
6.
It changes regularly in a period or a group.
Electronegativity of an element is important in determining the bond
character. If two atoms have the same electronegativities the bond between the
two will be covalent, while a large difference in electronegativity leads to
ionic bond. Between the extremes the purely covalent bond and purely ionic, the
bonds will have different degrees of ionic character. As a rough estimate it is
seen that a difference of 1.7 in electronegativities, the bond has 50% ionic
character. If the difference is less than 1.7, the bond is considered covalent,
and greater than 1.7 it is considered ionic.
Related Topics