Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Earlier periodic classification
Earlier periodic classification
More than one hundred and nine elements are known today,. The periodic
table of elements is an important landmark in the history of chemistry. It
would be difficult to study individually the chemistry of all the elements and
their numerous compounds. The periodic table provides a systematic and
extremely useful framework for organizing a lot of information available on the
chemical behaviour of the elements into a few simple and logical patterns. This
gave rise to the necessity of classifying the elements into various groups or
families having similar properties. This classification has resulted in the
formulation of periodic table. Periodic table may be defined as the
arrangements of various elements according to their properties in a tabular
form.
All earlier attempts on the classification of elements were based on
atomic mass. Several chemists have for long tried to classify the elements and
to find patterns in their properties.
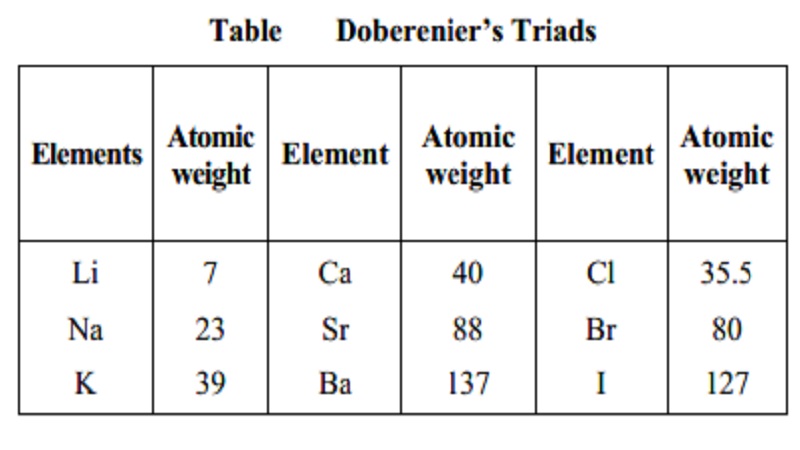
Dobereiner's Triads
In 1829, John Dobereiner (German Chemist)
classified elements having similar properties into groups of three. These
groups were called triads. According to this law when elements are arranged in
the order of increasing atomic mass in a triad, the atomic mass of the middle
element was found to be approximately equal to the arithmetic mean of the other
two elements. For example lithium, sodium and potassium constituted one triad.
However, only a limited number of elements could be grouped into traids.
Table Doberenier's Triads
Elements Atomic Element Atomic Element Atomic
weight weight weight
Li 7 Ca 40 Cl 35.5
Na 23 Sr 88 Br 80
K 39 Ba 137 I 127
Newlands Law of Octaves
In 1865, John Newlands (English Chemist) observed that if the elements
were arranged in order of their increasing atomic weights, the eighth element
starting from a given one, possessed properties similar to the first, like the
eighth note in an octave of music. He called it the law of octaves. It worked
well for the lighter elements but failed when applied to heavier elements.
Lother-Meyer's Arrangement
In 1869, J. Lother-Meyer in
Germany gave a more detailed and accurate relationship among the elements.,
Lother-Meyer plotted atomic volumes versus atomic weights of elements and
obtained a curve. He pointed out that elements occupying similar positions in
the curve possessed similar properties.
Mendeleev's Periodic Table
In 1869,
Dimitriv Mendeleev (Russian Chemist) arranged the 63 chemical elements, then
known, according to their increasing order of atomic weights. He gave his
famous scheme of the periodic classification of elements known as the periodic
law. The law states that ' the properties of the elements are the periodic
function of their atomic weights'. It means that when elements are arranged in
order of increasing atomic weights, the elements was similar properties recur
after regular intervals. On the basis of this periodic law Mendeleev
constructed a periodic table in such a way that the elements were arranged
horizontally in order of their increasing atomic weights. Mendeleev, while
studying his Periodic Table had found that in certain cases the regularity in
behaviour between two succeeding elements was not observed. In order to
overcome this he had kept gaps between such elements and had predicted that the
gaps would be filled by new elements, to be discovered in future, For example,
both gallium and germanium were not discovered at the time when Mendeleev
proposed the periodic table. Mendeleev named these elements as eka-aluminium
and eka-silicon because he believed that they would be similar to aluminium and
silicon respectively. These elements were discovered later and Mendeleev's
prediction proved remarkably correct. The discoveries / synthesis of new
elements have continued even to the present day, raising their number to 120.
The elements with atomic numbers upto 92 (i.e. uranium) are found in nature.
The rest known as transuranium elements have been synthesized in the
laboratories, which are highly unstable. They decay radioactively.
The modified periodic table is essentially similar to that of Mendeleev
with a separate column added for noble gases, which were not discovered until
the closing years of the nineteenth century. The general plan of the modified
Mendeleev's periodic table is improved.
The Mendeleev's modified periodic table consists of:
1.
Nine vertical columns called groups. These are
numbered from I to VIII and zero. (The members of zero group were not
discovered at the time of Mendeleev). Each group from I to VII is further
sub-divided into two sub-groups designated as A and B. Group VIII consists of
three sets, each one containing three elements. Group zero consists of inert
gases.
2.
Seven horizontal rows, called periods. These are
numbered from 1 to 7. First period contains two elements. Second and third
periods contain eight elements each. These periods are called short periods.
Fourth and fifth contains eighteen elements each. These periods are called long
periods. Sixth period contains thirty two elements and is called longest period.
Seventh period is incomplete and contains nineteen elements according to early
classification.
Related Topics