Preparation, Properties, Structure, Uses - Diborane | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Diborane
Diborane
Preparation:
As discussed earlier
diborane can be prepared by the action of metal hydride with boron.
This method is used for
the industrial production.
Diborane can also be
obtained in small quantities by the reaction of iodine with sodium borohydride
in diglyme.
2NaBH4 + I2
→ B2H6 +
2NaI + H2
On heating magnesium
boride with HCl a mixture of volatile boranes are obtained.
2Mg3B2
+ 12HCl → 6MgCl2 + B4H10 + H2
B4H10
+ H2 → 2B2H6
Properties:
Boranes are colourless
diamagnetic compounds with low thermal stability. Diborane is agas at room
temperature with sweet smell and it is extremely toxic. It is also highly
reactive.
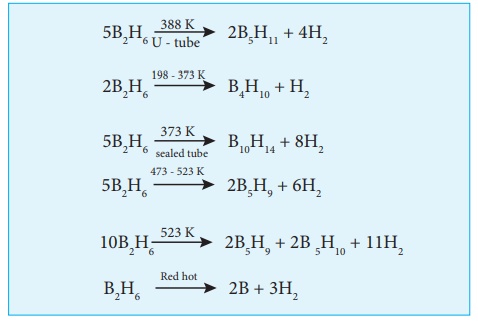
At high temperatures it
forms higher boranes liberating hydrogen.
Diboranes reacts with
water and alkali to give boric acid and metaborates respectively.
B2H6
+ 6H2O → 2H3BO3 + 6H2
B2H6
+ 2NaOH +2H2O → 2NaBO2 + 6H2
Action of air:
At room temperature pure
diborane does not react with air or oxygen but in impure form it gives B2O3
along with large amount of heat.
B2H6
+ 3O2 → B2O3
+ 3H2O
ΔH = -2165 KJ mol-1
Diborane reacts with
methyl alcohol to give trimethyl Borate.
B2H6
+ 6CH3 OH → 2B(OCH3)3+
6H2
Hydroboration:
Diborane adds on to
alkenes and alkynes in ether solvent at room temperature. This reaction is
called hydroboration and is highly used in synthetic organic chemistry,
especially for anti Markovnikov addition.
B2H6
+ 6RCH=CHR → 2B(RCH-CH2R)3
Reaction with ionic hydrides
When treated with metal
hydrides it forms metal borohydrides

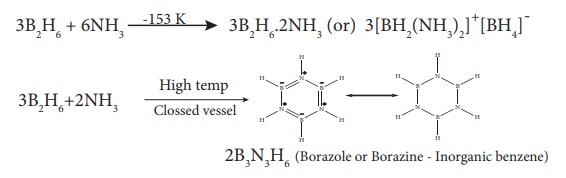
Reaction with ammonia:
When treated with excess
ammonia at low temperatures diborane gives diboranediammonate. On heating at
higher temperatures it gives borazole.
Structure of diborane:
In diborane two BH2
units are linked by two bridged hydrogens. Therefore, it has eight B-H bonds. However,
diborane has only 12 valance electrons and are not sufficient to form normal
covalent bonds. The four terminal B-H bonds are normal covalent bonds (two centre
- two electron bond or 2c-2e bond).
The remaining four
electrons have to be used for the bridged bonds. i.e. two three centred B-H-B
bonds utilise two electrons each. Hence, these bonds are three centre- two
electron bonds (3c-2e). The bridging hydrogen atoms are in a plane as shown in
the figure 2.3. In diborne, the boron is sp3 hybridised.
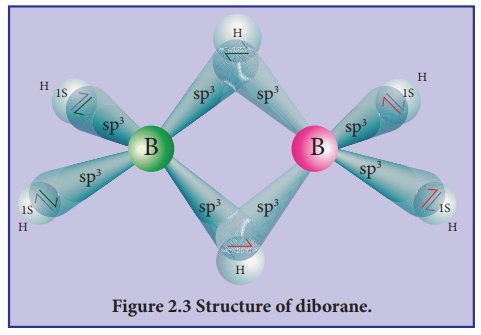
Three of the four sp3
hybridised orbitals contains single electron and the fourth orbital is empty.
Two of the half filled hybridised orbitals of each boron overlap with the two
hydrogens to form four terminal 2c-2e bonds, leaving one empty and one half
filled hybridised orbitals on each boron. The Three centre - two electron
bonds), B-H-B bond formation involves overlapping the half filled hybridised
orbital of one boron, the empty hybridised orbital of the other boron and the
half filled 1s orbital of hydrogen.
Uses of diborane:
·
Diborane is used as a high energy fuel for propellant
·
It is used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry
·
It is used in welding torches
Related Topics