Preparation, Properties, Structure, Uses - Carbon monoxide [CO] | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Carbon monoxide [CO]
Carbon
monoxide [CO]:
Preparation:
Carbon monoxide can be
prepared by the reaction of carbon with limited amount of oxygen.
2C + O2 → 2CO
On industrial scale
carbon monoxide is produced by the reaction of carbon with air. The carbon
monoxide formed will contain nitrogen gas also and the mixture of nitrogen and
carbon monoxide is called producer gas.
2C + O2/N2
(air) → 2CO + N2 ( Producers Gas)

The producer gas is then
passed through a solution of copper(I)chloride under pressure which results in
the formation of CuCl(CO).2H2O. At reduced pressures this solution
releases the pure carbon monoxide.
Pure carbon monoxide is
prepared by warming methanoic acid with concentrated sulphuric acid which acts
as a dehydrating agent.
HCOOH + H2SO4
→ CO + H2O + H2SO4
Properties
It is a colourless,
odourless, and poisonous gas. It is slightly soluble in water.
It burns in air with a
blue flame forming carbon dioxide.
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
When carbon monoxide is
treated with chlorine in presence of light or charcoal, it forms a poisonous
gas carbonyl chloride, which is also known as phosgene. It is used in the
synthesis of isocyanates.
CO + Cl2 → COCl2
Carbon monoxide acts as
a strong reducing agent.
CO + Fe2O3
→ 2Fe + 3CO2
Under high temperature
and pressure a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen (synthetic gas or syn
gas) gives methanol.
CO + 2H2 → CH3OH
In oxo process, ethene
is mixed with carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas to produce propanal.
CO + C2H4
+ H2 → CH3CH2CHO
Fischer Tropsch synthesis:
The reaction of carbon
monoxide with hydrogen at a pressure of less than 50 atm using metal catalysts
at 500 - 700 K yields saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
nCO + (2n+1)H2 →
CnH(2n+2) + nH2O
nCO + 2nH2 → CnH2n + nH2O
Carbon monoxide forms
numerous complex compounds with transition metals in which the transition meal
is in zero oxidation state. These compounds are obtained by heating the metal
with carbon monoxide.
Eg. Nickel tetracarbonyl
[Ni(CO)4], Iron pentacarbonyl [Fe(CO)5], Chromium
hexacarbonyl [Cr(CO)6].
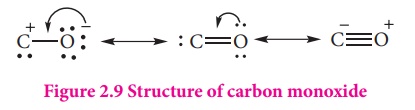
Structure:
It has a linear
structure. In carbon monoxide, three electron pairs are shared between carbon
and oxygen. The bonding can be explained using molecular orbital theory as
discussed in XI standard. The C-O bond distance is 1.128Å. The structure can be
considered as the resonance hybrid of the following two canonical forms.
Uses of carbon monoxide:
·
Equimolar mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide - water gas and
the mixture of carbon monoxide and nitrogen - producer gas are important
industrial fuels
·
Carbon monoxide is a good reducing agent and can reduce many metal
oxides to metals.
·
Carbon monoixde is an important ligand and forms carbonyl compound
with transition metals
Related Topics