Preparation, Properties, Structure, Uses - Carbon dioxide | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Carbon dioxide
Carbon
dioxide:
Carbon dioxide occurs in
nature in free state as well as in the combined state. It is a constituent of
air (0.03%). It occurs in rock as calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate.
Production
On industrial scale it
is produced by burning coke in excess of air.
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
ΔH = 394 kJ mol-1
Calcination of lime
produces carbon dioxide as by product.
CaCO3 → CaO +
CO2
Carbon dioxide is
prepared in laboratory by the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on metal
carbonates.
CaCO3 + 2HCl →
CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Properties
It is a colourless,
nonflammable gas and is heavier than air. Its critical temperature is 31⁰
C and can be readily liquefied.
Carbon dioxide is a very
stable compound. Even at 3100 K only 76 % decomposes to form carbon monoxide
and oxygen. At still higher temperature it decomposes into carbon and oxygen.

Reducing behaviour:
At elevated
temperatures, it acts as a strong reducing agent. For example,
CO2 + Mg → 2MgO
+ C
Water gas equilibrium:
The equilibrium involved
in the reaction between carbon dioxide and hydrogen, has many industrial
applications and is called water gas equilibrium.
CO2 + H2
↔ CO + H2O
Water gas
Acidic behaviour:
The aqueous solution of
carbon dioxide is slightly acidic as it forms carbonic acid.
CO2 + H2O
↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-
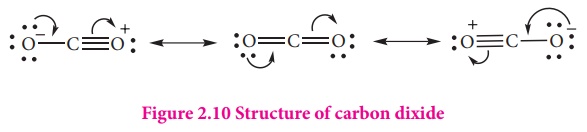
Structure of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide has a
liner structure with equal bond distance for the both C-O bonds. In this
molecule there is one C-O sigma bond. In addition there is 3c-4e bond covering
all the three atoms.
Uses of carbon dioxide
·
Carbon dioxide is used to produce an inert atomosphere for
chemical processing.
·
Biologically, it is important for photosynthesis.
·
It is also used as fire extinguisher and as a propellent gas.
· It is used in the production of carbonated beverages and in the production of foam.
Related Topics