Preparation, Properties, Structure, Uses - Boric acid | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : p-Block Elements-I
Boric acid
Boric acid [H3BO3 or B(OH)3]:
Preparation:
Boric acid can be extracted from borax and colemanite.
Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5H2O → Na2SO4 + 4H3BO3
Ca2B6O11 + 11H2SO4 + SO2 → Ca(HSO3)2+ 6H3BO3
Properties:
Boric acid is a colourless transparent crystal. It is a very weak monobasic acid and, it accepts hydroxyl ion rather than donating proton.
B(OH)3 + 2H2O ↔ H3O+ + [B(OH)4]-

It reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium metaborate and sodium tetraborate.
NaOH + H3BO3 → NaBO2 + 2H2O
2NaOH + 4H3BO3 → Na2B4O7+ 7H2O
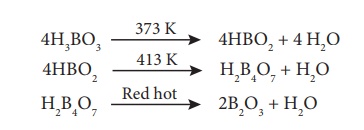
Action of Heat:
Boric acid when heated at 373 K gives metaboric acid and at 413 K, it gives tetraboric acid.
When heated at red hot, it gives boric anhydride which is a glassy mass.
Acton of ammonia
Fusion of urea with B(OH)3, in an atmosphere of ammonia at 800 - 1200 K gives boron nitride.
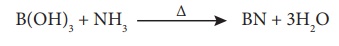
When boric acid or borate salt is heated with ethyl alcohol in presence of conc. sulphuric acid, an ester, trialkylborate is formed. The vapour of this ester burns with a green edged flame and this reaction is used to identify the presence of borate.
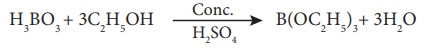
Note: The trialkyl borate on reaction with sodium hydride in tetrahydrofuron to form a coordination compound Na[BH(OR)3], which acts as a powerful reducing agent.
Formation of boron trifluoride:
Boric acid reacts with calcium fluoride in presence of conc. sulphuric acid and gives boron trifluoride.
3CaF2 + 3H2SO4 + 2 B(OH)3 → 3CaSO4 + 2BF3 + 6H2O
Borax when heated with soda ash it gives borax
Na2CO3 + 4B(OH)3 → Na2B4O7 + CO2 + 6H2O
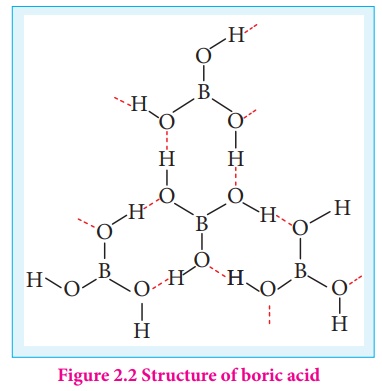
Structure of Boric acid:
Boric acid has a two dimensional layered structure. It consists of [BO3]3-unit and these are linked to each other by hydrogen bonds as shown in the Figure 2.2.
Uses of boric acid:
1. Boric acid is used in the manufacture of pottery glases, enamels and pigments.
2. It is used as an antiseptic and as an eye lotion.
3. It is also used as a food preservative.
Related Topics