Applied Statistics - Choose the correct Answer | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 9 : Applied Statistics
Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 9 : Applied Statistics
Choose the correct Answer
Choose the correct Answer
1. A time series is a set of data
recorded
(a) Periodically
(b) Weekly
(c) successive points of time
(d)
all the above
2. A time series consists of
(a) Five components
(b)
Four components
(c) Three components
(d) Two components
3. The components of a time series which
is attached to short term fluctuation is
(a)
Secular trend
(b) Seasonal variations
(c) Cyclic variation
(d)
Irregular variation
4. Factors responsible for seasonal
variations are
(a) Weather
(b) Festivals
(c) Social customs
(d)
All the above
5. The additive model of the time series
with the components T, S, C and I is
(a) y=T+S+C×I
(b) y=T+S×C×I
(c)
y=T+S+C+I
(d) y=T+S×C+I
6. Least square method of fitting a
trend is
(a)
Most exact
(b) Least exact
(c) Full of subjectivity
(d) Mathematically unsolved
7. The value of ‘b’ in the trend line y=a+bx
is
(a) Always positive
(b) Always negative
(c)
Either positive or negative
(d) Zero
8. The component of a time series
attached to long term variation is trended as
(a) Cyclic variation
(b)
Secular variations
(c) Irregular variation
(d) Seasonal variations
9. The seasonal variation means the
variations occurring with in
(a) A number of years
(b)
within a year
(c) within a month
(d) within a week
10. Another name of consumer’s price
index number is:
(a) Whole-sale price index number
(b)
Cost of living index
(c) Sensitive
(d) Composite
11. Cost of living at two different
cities can be compared with the help of
(a)
Consumer price index
(b) Value index
(c) Volume index
(d) Un-weighted index
12. Laspeyre’s index = 110, Paasche’s
index = 108, then Fisher’s Ideal index is equal to:
(a) 110
(b) 108
(c) 100
(d)
109
13. Most commonly used index number is:
(a) Volume index number
(b) Value index number
(c)
Price index number
(d) Simple index number
14. Consumer price index are obtained
by:
(a) Paasche’s formula
(b) Fisher’s ideal formula
(c) Marshall Edgeworth formula
(d)
Family budget method formula
15. Which of the following Index number
satisfy the time reversal test?
(a)Laspeyre’s Index number
(b) Paasche’s Index number
(c)
Fisher Index number
(d) All of them.
16. While computing a weighted index,
the current period quantities are used in the:
(a) Laspeyre’s method
(b)
Paasche’s method
(c)
Marshall Edgeworth method
(d) Fisher’s ideal method
17. The quantities that can be
numerically measured can be plotted on a
(a) p - chart
(b) c – chart
(c)
x bar chart
(d) np – chart
18. How many causes of variation will
affect the quality of a product?
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c)
2
(d) 1
19. Variations due to natural disorder
is known as
(a)
random cause
(b) non-random cause
(c) human cause
(d) all of them
20. The assignable causes can occur due
to
(a) poor raw materials
(b) unskilled labour
(c) faulty machines
(d)
all of them
21. A typical control charts consists of
(a) CL, UCL
(b) CL, LCL
(c)
CL, LCL, UCL
(d) UCL, LCL
22. ![]() chart is a
chart is a
(a) attribute control chart
(b)
variable control chart
(c) neither Attribute nor variable
control chart
(d) both Attribute and variable control
chart
23. R is calculated using
(a)
xmax − xmin
(b) xmin − xmax
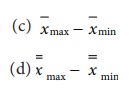
24. The upper control limit for ![]() chart is given by
chart is given by
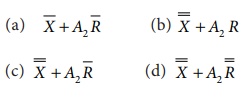
Ans:
(c)
25. The LCL for R chart is given by
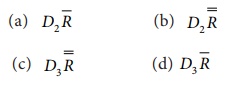
Ans:
(d)
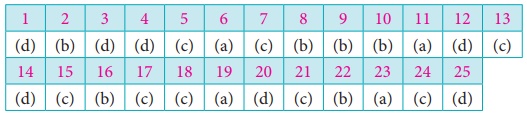
Related Topics