Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Chemical Bonding: Concept of Resonance
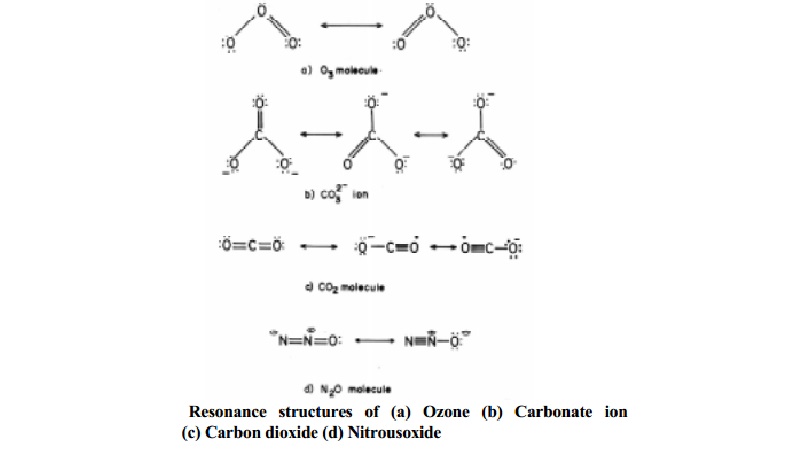
Concept of Resonance
According to the concept of resonance whenever a
single Lewis structure cannot describe a molecular structure accurately, a
number of structures with similar energy, positions of nuclei, bonding and non
bonding pairs of electrons are considered to represent the structure. Each such
structure is called as canonical structure. A resonance hybrid consists of many
canonical structures. All the canonical structures are equally possible to
represent the structure of the molecule.
For
example, in ozone (O3) molecule, the two canonical structures as shown below
and their hybrid represents the structure of O3 more accurately.
Resonance is represented by a double headed arrow placed between the canonical
structures. There are two canonical forms of O3.
The resonance structures are possible for molecular ions also. For
example, consider resonance in CO32- ion:-
The single
Lewis structure based on the presence of two single bonds and one double bond
between each carbon and oxygen atoms is inadequate to represent the molecule
accurately as it represents unequal bonds. According to experimental findings
all carbon to oxygen bonds in CO32- are equivalent. Therefore
the carbonate ion is best described as a resonance hybrid of the canonical
forms as shown in Fig. b.
There are three canonical forms of CO32-.
Structure of CO2 molecule is also an example of resonance, the
experimental C-O bond length is found to be shorter than C-O single bond length
and longer than C=O bond length and lies intermediate in value between a pure
single and a pure double bond lengths. Also the two C=O bond length in the CO2
molecule are equivalent and the properties of the two bonds are also the same.
Therefore, a single lewis structure cannot depict the structure of CO2
as a whole and it is best described as a resonance hybrid of the canonical
forms given in Fig. c.
In N2O molecule which is a linear
molecule, structures with charges on atoms can be written similar to CO2.
Here also the experimental bond length of N-N-bond lies between a double and triple bond and that of N-O bond length lies between a single and a double bond. Therefore N2O exists as a hybrid structure of the two canonical forms with a linear geometry.
Related Topics