Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 6 : Gaseous State
Application of DaltonŌĆÖs law
Application of DaltonŌĆÖs law
In a reaction involving the collection of gas by downward displacement of water, the pressure of dry vapor collected can be calculated using DaltonŌĆÖs law.
Pdry gas collected = ptotal - pwater vapour
pwater vapour is generally referred as aqueous tension and its values are available
for air at various temperatures.
Let us understand Dalton's law by solving this problem. A mixture of gases contains 4.76 mole of Ne, 0.74 mole of Ar and 2.5 mole of Xe. Calculate the partial pressure of gases, if the total pressure is 2 atm. at a fixed temperature.
Solution:
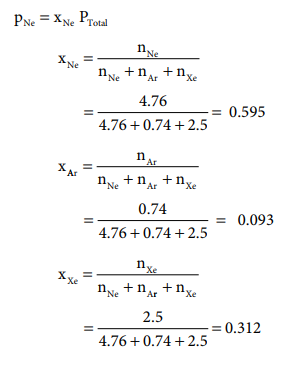
PNe = xNe PTotal = 0.595 ├Ś 2
= 1.19 atm.
PAr = xAr PTotal = 0.093 ├Ś 2
= 0.186 atm.
PXe = xXe PTotal = 0.312 ├Ś 2
= 0.624 atm.
Related Topics