Chapter: Biochemistry: The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins
Two Types of Protein Conformations: Fibrous and Globular
Two Types of Protein Conformations: Fibrous and Globular
It is difficult to draw a clear separation between secondary and tertiary structures. The nature of the side chains in a protein (part of the tertiary structure) can influence the folding of the backbone (the secondary structure). Comparing collagen with silk and wool fibers can be illuminating. Silk fibers consist largely of the protein fibroin, which, like collagen, has a fibrous structure, but which, unlike collagen, consists largely of β-sheets. Fibers of wool consist largely of the protein keratin, which is largely α-helical. The amino acids of which collagen, fibroin, and keratin are composed determine which conformation they will adopt, but all are fibrous proteins (Figure 4.12a).
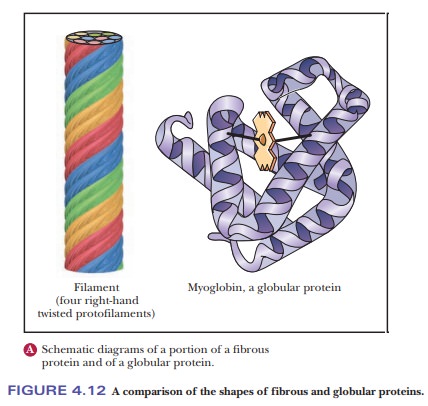
In other proteins, the backbone folds back on itself to produce a more or less spherical shape. These are called globular proteins (Figure 4.12b), and we shall see many examples of them.
Their helical and pleated-sheet sections can be arranged so as to bring the ends of the sequence close to each other in three dimensions. Globular proteins, unlike fibrous proteins, are water-soluble and have compact structures; their tertiary and quaternary structures can be quite complex.
Related Topics