Chapter: Ophthalmology: Retina
Posterior Uveitis Due to Toxoplasmosis - Retinal Inflammatory Disease
Posterior Uveitis Due to Toxoplasmosis
Definition
Focal chorioretinal inflammation caused by
infection.
Epidemiology:
This clinical syndrome is encountered frequently.
Pathogenesis:
The pathogen,Toxoplasma
gondii, is transmittedby ingestionof
tissue cysts in raw or undercooked meat or by oocysts from cat feces. In con-genital toxoplasmosis, the child
acquires the pathogen through transplacen-tal transmission.
Symptoms and diagnostic considerations:
As a general rule, a negativecomplement-fixation
test does not exclude Toxoplasma
infection where clas-sic clinical symptoms are present. Both forms of the
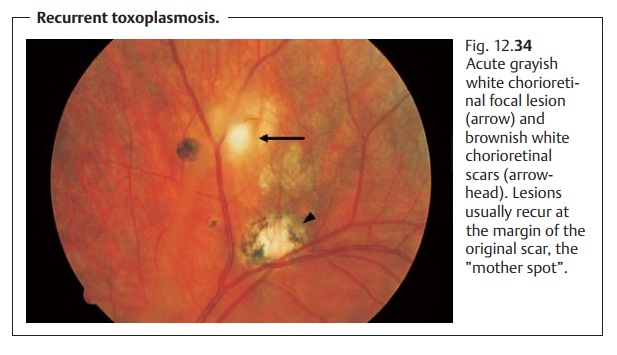
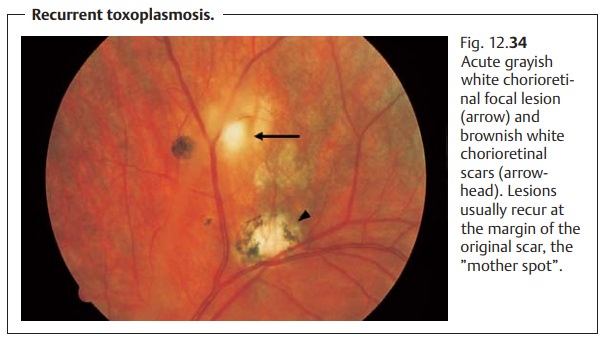
disorder present with characteristic grayish
white chorioretinal focal lesions surrounded by vitreousinfiltration and associated vasculitis (Fig. 12.34). Incongenital toxoplasmosis,the affected children have a macular scar that significantly impairs visual acu-ity. This often leads to secondary
strabismus. Intracerebral involvement can also result in hydrocephalus and
intracranial calcifications. In the acquiredform,
visual acuity is impaired only where the macula is involved. This israrely the
case.
Congenital toxoplasmosis results in a macular
scar that significantly impairs visual acuity.
Differential diagnosis:
Chorioretinitis with tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, bor-reliosis
(Lyme disease), or syphilis should be excluded by serologic studies.
Treatment:
The treatment of choice consists of a combination
ofpyrimethamine, sulfonamide, folinic acid, and steroids in their respective
standard doses.
Prophylaxis:
Avoid raw meat and cat feces.
Clinical course and prognosis:
Posterior uveitis due to toxoplasmosis usu-ally heals without
severe loss of visual acuity where the macula is not involved. However, it can
recur at any time. There is no cure for the congenital form.
Related Topics