Chapter: Microbiology
Filariasis
FILARIASIS
Introduction
Filariasis are vector borne human parasitic diseases with com-plex life cycle. They are caused by nematodes. In their mature stage they reside in lymphatic system or in connective tissues. Adult parasite itself can provoke inflammatory reactions in tissues. They produce large numbers of larvae called microfilariae .
Human Filarial Species
There are eight filarial species in which humans are the definitive hosts
Species Causing LYMPHATIC FILARIASIS
Wuchereria bancrofti
Brugia malayi
Brugia timori
ONCHOCERCIASIS- RIVERBLINDESS
Onchocerca volvulus
EYE WORM DISEASE
Loa loa
OTHER SPECIES ( Generally considered to be non pathogens)
Mansonella ozzardi - causes pruritus
Mansonella perstans - causes localized angio edema and pruritus and neurological symptoms
Mansonella streptocerca - cause pruritus, rash, hypopigmentation
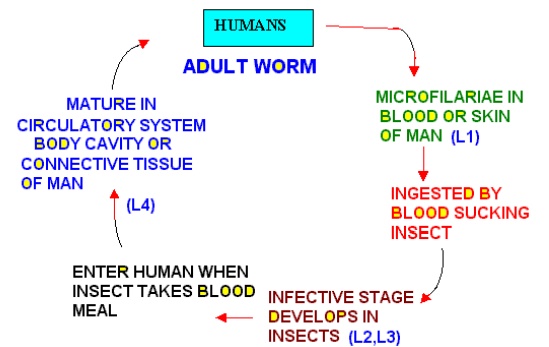
Life Cycle of Human Filarial Worms
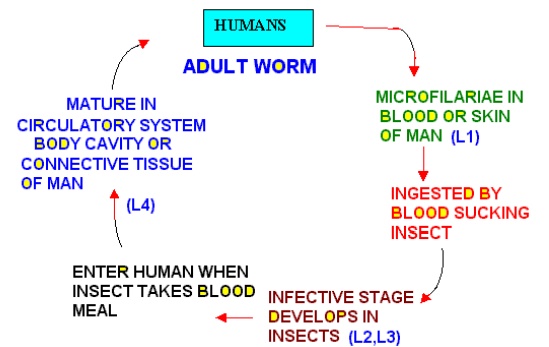
Adult Filarial Worms
· Filarial worms are arthropod –transmitted parasites
· They inhabit lymphatic subcutaneous and cutaneous tissues of humans
· Adult male is smaller than females
· Adults are sequestered in the tissues
· All female worms produce primitive larvae called “microfi-lariae”
Microfilariae
· These microfilariae are found in peripheral blood or in the skin
· They relatively simple in their organization and structure
· They are vermiform
· In stained preparations they appear to be composed of a col-umn of nuclei
These nuclei are interrupted along their length by spaces and special cells
These cells are precursors of body organelles.
Some species of mf are enveloped in sheath others do not have sheath
Filarial Parasites Location Disease
Wuchereria bancrofti Lymphatics Elephantiasis
Brugia malayi Lymphatics Elephantiasis
Brugia timori Lymphatics Elephantiasis
Loa Loa EyeSubcutaneous Calabar Swelling
Onchocerca Subcutaneous Onchocercomata
volvulus
Mansonella Abdominal Cavity Mild Allergic
perstansReactions
Mansonella Body Cavity
ozzardi
Mansonella Subcutaneous Fat
streptocerca Subcutaneous
Lymphatic Filariasis
The following clinical manifestations may be seen
1. Asymptomatic dsease
2. Filarial fevers
3. Chronic disease
4. Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia
Asymptomatic Disease
· Commonly seen in endemic areas
· Frequently associated with Bancroftian and Brugian filariasis
· Infected individuals never become symptomatic
· Many chronically infected persons are amicrofilaraemic
Filarial Fevers: Initially
1. Acute attacks of fever chills and malaise seen
2. It lasts for 3-15 days each
3. It is associated with retrograde adenolymphangitis
4. This can occur several times a year
5. Lymphadenitis affects commonly groin and axilla
6. In men infected with W.bancrofti
a. Lymph vessels of genitalia are affected
b. This leads to funiculitis, architis, epididymitis
Chronic Disease
· Occurs after 10-15 years of filarial fever (6months in non endemic persons)
· Episodes of chronic obstructive disease due to damages to lymph vessels seen
· Reversible lymphedema of legs, scrotum, arms, penes, or breasts present
§ This may progress to elephantiasis
· Chyluria results from rupture of renal lymph vessels
· Hydrocele is due to recurrent architis
Tropical Pulmonary Eosinophilia
· It is a well recognized clinical entity in India and Singapore
· It is attributed to occult filarial infection
· It is characterized by paroxysmal nocturnal asthma and cough
· It is associated with high eosinophilia
· Can be relieved by DEC
· There is high titer of antibodies to microfilariae
· Microfilariae have been demonstrated in the lung
· Small eosinophilic granulomas with mf are scattered throughout the lung
· This condition may have resulted from altered host response to parasite, resulting in allergic phenomenon manifested by persistent hyper eosinophilia and pulmonary symptoms
Laboratory Diagnosis Of Filariasis
Specimens to be collected
1. Blood : Nocturnal species/area – Night blood 10-12pm : Diurnal - Day time
2. Chyluric urine:
3. Exudate of lymph varix
4. Hydrocele fluid
5. Lymph node biopsy – not recommended for pure diagnostic purpose
6. Ultrasound examination: shows characteristics filarial dance
Examination of blood and other body fluids
1. By thick smear examination
2. By thin smear examination Giemsa stained smears
3. Saponin lysis and centrifugation- staining
4. Knott concentration method
5. Membrane filter concentration.
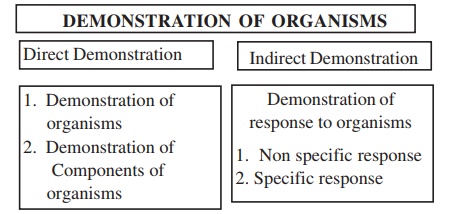
Demonstration of Components of the organisms
1. Precipitation using antisera
2. Counterimmuno Electrophoresis
3. Elisa
4. PCR
Demonstration of response to organisms
Responses include Non specific responses and Specific responses
Non specific responses
1. Filarial lymphangitis- must be differentiated from bacterial lymphangitis
2. Chronic lymphedema-
May also be caused by malignancy, renal and cardiac failure, post operative changes, congenital malformations
3. Architis and epidydymitis
In sexully transmitted diseases also these may be present
4. Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia
May be confused with Loeffler’s syndrome, Broncho pulmonary aspergillosis, eosinophilic pneumonia, drug reactions, other parasitic infections(Hook worms, Ascaris, Stongyloides).
Typical clinical history, exposure in appropriate areas, response to DEC will help with the diagnosis
Specific responses
1. Humoral immune responses
a. Antibody response
b. Hypersensitivity response
2. Cell mediated immune responses
a. CMI
b. CM hypersensitivity responses
Antibody responses
Antibodies can be detected by the following tests
In the past:
1. Gel diffusion
2. Complement fixation
3. Indirect immunofluorescence assays
4. indirect haemagglutination test
5. ELISA test
Related Topics