Chapter: Cryptography and Network Security
Viruses And Related Threats
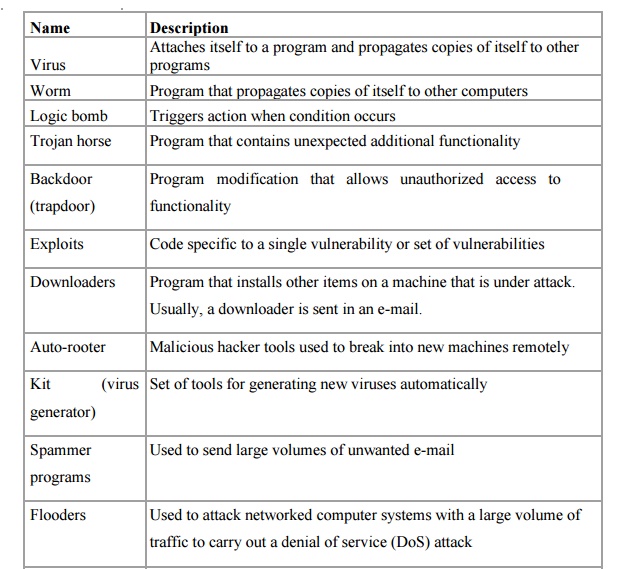
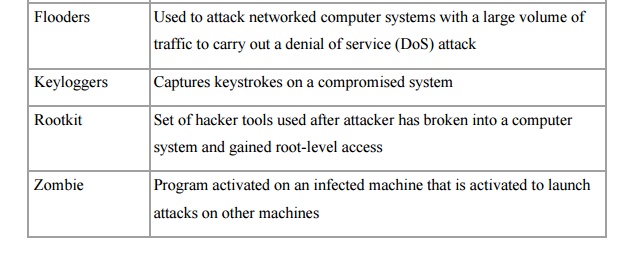
VIRUSES AND RELATED THREATS
Perhaps
the most sophisticated types of threats to computer systems are presented by
programs that exploit vulnerabilities in computing systems.
1. Malicious Programs
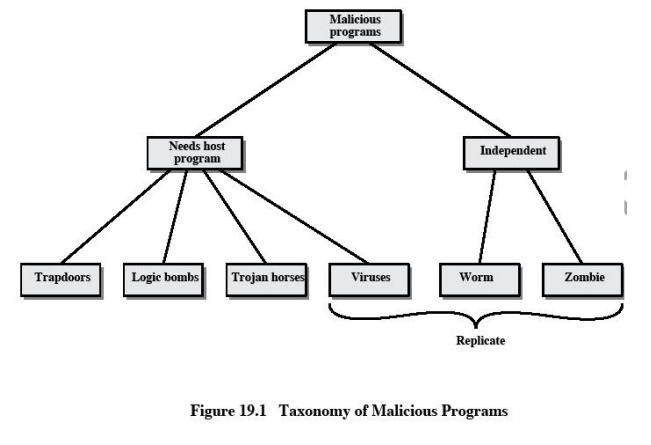
Malicious
software can be divided into two categories:
those
that need a host program, and those that are independent.
The
former are essentially fragments of programs that cannot exist independently of
some actual application program, utility, or system program. Viruses, logic
bombs, and backdoors are examples. The latter are self-contained programs that
can be scheduled and run by the operating system. Worms and zombie programs are
examples.
2. The Nature of Viruses
A virus
is a piece of software that can "infect" other programs by modifying
them; the modification includes a copy of the virus program, which can then go
on to infect other programs.
A virus
can do anything that other programs do. The only difference is that it attaches
itself to another program and executes secretly when the host program is run.
Once a virus is executing, it can perform any function, such as erasing files
and programs.
During
its lifetime, a typical virus goes through the following four phases:
·
Dormant
phase: The virus is idle. The virus will eventually be activated by some
event, such as a date, the presence
of another program or file, or the capacity of the disk exceeding some limit.
Not all viruses have this stage.
·
Propagation
phase: The virus places an identical copy of itself into other programs or into certain system areas on the disk.
Each infected program will now contain a clone of the virus, which will itself
enter a propagation phase.
·
Triggering
phase: The virus is activated to perform the function for which it was intended. As with the dormant phase,
the triggering phase can be caused by a variety of system events, including a
count of the number of times that this copy of the virus has made copies of
itself.
·
Execution
phase: The function is performed. The function may be harmless, such as a message on the screen, or damaging,
such as the destruction of programs and data files.
3. Virus Structure
A virus
can be prepended or postpended to an executable program, or it can be embedded
in some other fashion. The key to its operation is that the infected program,
when invoked, will first execute the virus code and then execute the original
code of the program.
An infected program begins with the virus code and
works as follows.
The first
line of code is a jump to the main virus program. The second line is a special
marker that is used by the virus to determine whether or not a potential victim
program has already been infected with this virus.
When the
program is invoked, control is immediately transferred to the main virus
program. The virus program first seeks out uninfected executable files and
infects them. Next, the virus may perform some action, usually detrimental to
the system.
This
action could be performed every time the program is invoked, or it could be a
logic bomb that triggers only under certain conditions.
Finally,
the virus transfers control to the original program. If the infection phase of
the program is reasonably rapid, a user is unlikely to notice any difference
between the execution of an infected and uninfected program.
A virus
such as the one just described is easily detected because an infected version
of a program is longer than the corresponding uninfected one. A way to thwart
such a simple means of detecting a virus is to compress the executable file so
that both the infected and uninfected versions are of identical length.. The
key lines in this virus are numbered. We assume that program P1 is
infected with the virus CV. When this program is invoked, control passes to its
virus, which performs the following steps:
1.
For each uninfected file P2 that is
found, the virus first compresses that file to produce P'2, which is
shorter than the original program by the size of the virus.
2.
A copy of the virus is prepended to the compressed
program.
3.
The compressed version of the original infected
program, P'1, is uncompressed.
4.
The uncompressed original program is executed.
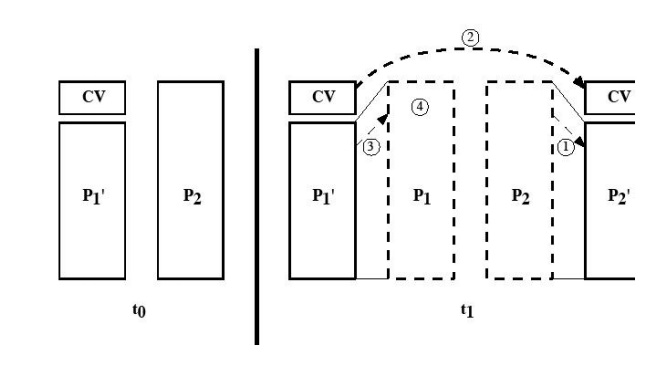
In this
example, the virus does nothing other than propagate. As in the previous example,
the virus may include a logic bomb.
4. Initial Infection
Once a
virus has gained entry to a system by infecting a single program, it is in a
position to infect some or all other executable files on that system when the
infected program executes. Thus, viral infection can be completely prevented by
preventing the virus from gaining entry in the first place. Unfortunately,
prevention is extraordinarily difficult because a virus can be part of any
program outside a system. Thus, unless one is content to take an absolutely
bare piece of iron and write all one's own system and application programs, one
is vulnerable.
Related Topics