Chapter: Artificial Intelligence
Type of Knowledge
TYPE OF KNOWLEDGE
The categorisation of knowledge is very much large and interesting. They
can be of following types:
Declarative knowledge
It is the passive knowledge expressed as statements of facts about the
world. It gives the simple facts and ideas about any phenomenon. It means just
the representation of facts or assertions. This tells the total description
about the situation. For example, the facts about an organization may be its
buildings, location, no. of departments, no. of employees etc. The facts may be
of two types i.e. static and dynamic. The static facts do not change with time
where as the dynamic facts change with time. For example, the name and location
of an organization is permanent. But some additional departments may be added.
Procedural knowledge
Procedural knowledge is the compiled knowledge related to the
performance of some task. For example the steps used to solve an algebric equation
can be expressed as procedural knowledge. It also eradicates the limitations of
declarative knowledge i.e. declarative knowledge tells about the organization
but it cannot tell how the employees are working in that organization and how
the products are developed. But procedural knowledge describes everything about
the organization by using production rules and dynamic attributes.
For example, If: All the employees are very hardworking
They are very punctual
They have productive ideas.
Then: Large no. of products can be produced within a very limited time
period.
The advantages of using procedural knowledge are as follows:
1)
Domain specific knowledge can be
easily represented.
2)
Extended logical inferences, such
as default reasoning facilitated.
3) Side effects of actions may be modeled. Some
disadvantages of procedural knowledge are
1)
Completeness: In procedural knowledge not all cases may be
represented.
2)
Consistency:Not all deductions
may be correct.
3) Modularity: Changes in
knowledge base might have far-reaching effects.
Inheritable knowledge
There are many situations in the world, where the object of an event
inherits some properties of that particular event or any other event.
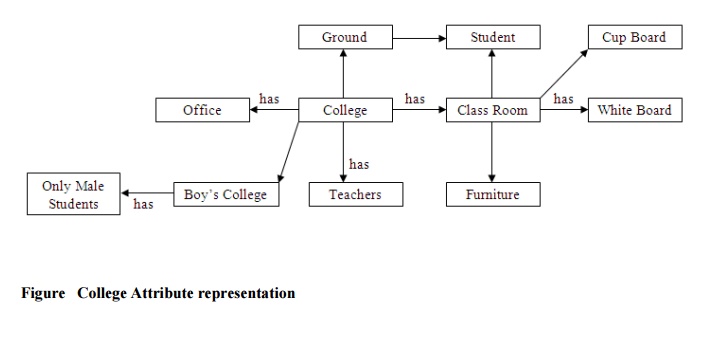
For example, consider a college. A college has certain features like
classrooms, teachers, play ground, furniture, students etc. Besides these,
there will be some general concepts regarding the functioning of the college,
like it will have time table for each class, a fee deposit plan, examination
pattern, course module etc. It can have many more deep concepts like placement
of students etc. Now, if we say ŌĆ£A is a Colleg eŌĆØ, then A will automatically
inherits all the features of the college. It may be possible that X has some
additional features. The inheritable knowledge is diagrammatically represented
below. Here, the relationship ŌĆśhasŌĆÖ
indicates the silent features or attributes and ŌĆśis aŌĆÖ represents the variable or instance of that type. A inherits
all the properties of college and has one additional feature of having male
students. In this type of knowledge, data must be organized into a hierarchy of
classes. The arrows represent the point from object to its value in the
diagram. Boxed nodes represent the objects and values of attributes of objects.
Relational
Knowledge
Relational knowledge is made up of objects
consisting of attributes and corresponding associated values. In this type of
knowledge, the facts are represented as set of relations in a tabular form. The
table stores or captures all the hidden attributes of objects.
For example the knowledge about doctors may be as mentioned in figure .
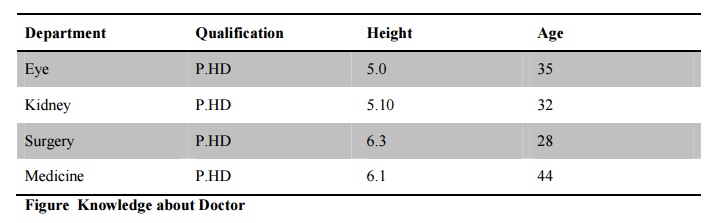
Figure
Knowledge about Doctor
This form of representation is the simplest and can
be used in database systems. But this representation cannot store any semantic,
information. For example, from this information we cannot answer the questions
like ŌĆ£What is the name of the doctorŌĆØ? or ŌĆ£How many doctors are in eye
departmentŌĆØ?
Inferential
Knowledge
The knowledge, which can use inference mechanism to
use this knowledge is called inferential knowledge. The inheritance property is
a very powerful form of inferential knowledge. The inference procedures
implement the standard logic rules of inference. There are two types of inference
procedures like forward inference and backward inference. Forward inference
moves from start state to goal state whereas backward inference moves from goal
state to start state. In this type of knowledge several symbols are generally
used like " (universal quantifier), $(existential quantifier), ® (arrow
indicator) etc.
For example: All cats have tails
" X: cat (x) ® has tail (x)
Advantages:
1)
A set of strict rules are defined
which can be used to derive more facts.
2)
Truths of new statements can be
verified.
3)
It gives guarantee about the
correctness.
4)
Many inference procedures
available to implement standard rules of logic.
Heuristic Knowledge
This type of knowledge is fully experimental. This knowledge requires
some judgments about any performance. One can guess a good thing and also one
can think bad thing. But good performances are generally taken in heuristic
knowledge. For example, suppose it is asked that ŌĆ£Ram will score how much
percentage in his final semester?ŌĆØ Then the answer might be 80%, 70%, 30% or
95%. The individual answers of this question based on the heuristic knowledge.
The answer would be based on various factors such as past performance, his
talent etc. If his previous semester percentage was 78%, then if one will say
he will secure 10% in this semester then obviously he has not any knowledge
about Ram.
Tacit Knowledge
This kind of knowledge is acquired by experience. Tacit knowledge is
subconsciously understood and applied, difficult to articulate and formalize.
This type of knowledge is developed from direct experience and action. This
knowledge is usually shared through highly interactive conversation, story
telling and experience. It also includes cognitive skills such as intuition as
well as technical skills such as craft and know-how. Tacit knowledge cannot be
transmitted before it is converted into words, models or numbers that can be
understood. Tacit knowledge can be defined in two dimensions, such as technical
dimension and cognitive dimension. In technical dimension highly subjective and
personal insights, intuitions and inspirations derived from long experience.
The dimensions such as beliefs, ideals, principles, values and emotions fall in
the category of cognitive dimension.
Explicit Knowledge
This knowledge is formalized, coded in several natural languages
(English, Italian and Spanish) or artificial languages (UML, Mathematics etc).
This knowledge can be easily transmitted. It includes theoretical approaches,
problem solving, manuals and database. As explicit knowledge, it was the first
to be or, at least, to be archived. Tacit and explicit knowledge are not
totally separate, but mutually complementary entities. Without any experience,
we cannot truly understand. Explicit knowledge is playing an increasingly large
role in organization and it is considered by some to be the most important
factor of production in the knowledge economy. Imagine an organization without
procedure manuals product literature or computer software. Also with explicit
knowledge, some tacit knowledge is required to run the business in an
organization. Without explicit knowledge, the organization is simply has a zero
performance.
Research Knowledge
There are many standards for the generation and critical appraisal of
research knowledge, but judging the quality of knowledge in this source is not
without difficulty. There are disputes about the nature and content of
standards in areas such as qualitative research, and the implementation of
standards is sometimes weak so that conformity with them is not necessarily a
guarantee of quality. This type of knowledge is very useful for researchers to
improve the research quality.
Related Topics