Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Thermodynamics: Work, heat and energy
Work, heat and energy
In order
to formulate the laws of
1 Torr = 1 mm of Hg
thermodynamics it becomes necessary to know the properties and nature of
work (w) heat (q) and energy (u).
Work (w)
In thermodynamics work is generally defined as
the force (F) multiplied by the distance of displacement(s). That is,
w = F.s.
Several aspects should be considered in the
definition of work which are listed below:
1.
work appears only at the boundary of the system.
2.
work appears during the change in the state of
the system.
3.
work brings in a permanent effect in the
surroundings.
4.
work is an algebraic quantity.
5.
work is a path function and it is not a state
function.
Types of work
Many types of work are known. Some of the types
of work are as follows:
(i)
Gravitational work
This work is said to be done when a body is raised to a certain height
against the gravitational field. If a body of mass `m' is raised through a
height `h' against acceleration due to gravity `g', then the gravitational work
carried out is `mgh'. In this expression, force is `mg' and the distance is
`h'.
(ii) Electrical work
This type of work is said to be done when a charged body moves from one
potential region to another. The electrical work is Q .V. if V is the potential
difference causing the quantity of electricity 'Q' during its movement
(iii) Mechanical work
This type of work is associated with changes in
volume of a system when an external pressure is applied or lowered. This
pressure-volume work is also referred to as the mechanical work.
Heat
Like work, heat (q) is regarded in
thermodynamics as energy in transit across the boundary separating a system
from its surroundings. Heat changes result in temperature differences between
system and surroundings. Heat cannot be converted into work completely without
producing permanent change either in the system or in the surroundings. Some of
the characteristics of heat (q) are:
heat is an algebraic quantity.
heat is a path function and is not a state function.
heat changes are generally considered as temperature changes of the
system.
Sign
convention for heat (q) and work (w)
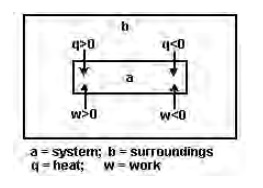
when, (i) heat is absorbed by the system (or) heat is lost by
surroundings to the system: +q
1.
heat is evolved by the system (or) heat is
gained by surroundings: -q.
2.
work is done by the system : -w
3.
work is done on the system : +w
If heat (q) is supplied to the system, the energy of the system
increases and `q' is written as a positive quantity. If work is done on the
system, the energy of the system increases and `w' is written as a positive
quantity. When w or q is positive, it means that energy has been supplied to
the system as work or as heat. In such cases internal energy (U) of the system
increases. When w or q is negative, it means that energy is lost by the system
as work or as heat. In such cases, the internal energy (U) of the system
decreases.
Energy `U'
Energy is easily, defined as the capacity to do
work. Whenever there is a change in the state of matter of a system, then there
is a change in energy û8 of the system. For example energy changes are involved in processes like melting, fusion, sublimation, vapourisation
etc. of the matter in a system. Energy (U) exists in many forms. Kinetic energy
(K.E.) arises due to motion of a body and potential energy (P.E.) arises due to
its position in space.
In chemical systems, there are two types of energy available. The
energies acquired by the system like electrical, magnetic, gravitational etc.
and termed as external energies of the system. The internal energy is generally
referred to as the energy (U) of a thermodynamic system which is considered to
be made up of mainly by P.E. and K.E.
Characteristics of energy (U) are:
1.
U is a state function. Its value depend on the
initial and final states of the system.
2.
U is an extensive property. Its magnitude depend
on the quantity of material in the system.
3.
(iii) U is not a path function. Its value
remains constant for fixed initial and final states and does not vary even
though the initial and final states are connected by different paths.
In S.I. system the unit of energy is Joules `J'
or kJ.
Related Topics