Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Theories Of Coordination Compounds: Werner's theory, Valence bond theory
THEORIES OF COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
1 Werner's Theory
Alfred Werner (1866-1919) French born Swiss chemist
founded the modern theory on coordination compounds. His theory and pioneering
experimental work on metal complexes
won for him the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1913. Werner was the first
inorganic chemist to be awarded the nobel prize in chemistry. He is considered
at "Father of coordination chemistry".
Brief concepts of Werner's theory of coordination
compounds
Alfred Werner studied the structure of coordination
complexes and put forward his ideas
in the year 1893 which were known as 'Werner's coordination theory.
Postulates of Werner's theory
1.Every metal atom has two types of valencies
i) Primary valency or ionisable valency
ii) Secondary valency or non ionisable valency
2.The primary valency corresponds to the oxidation state
of the metal ion.
The primary valency of the metal ion is always satisfied
by negative ions.
3.Secondary valency corresponds to the coordination
number of the metal
ion or atom. The secondary valencies may be satisfied by
either negative ions or neutral
molecules.
4.The molecules or ion that satisfy secondary valencies
are called ligands.
5.The ligands which satisfy secondary valencies must
project in definite
directions in space. So the secondary valencies are
directional in nature whereas the
primary valencies are non-directional in nature.
6.The ligands have unshared pair of electrons. These
unshared pair of electrons
are donated to central metal ion or atom in a compound.
Such compounds are called coordination compounds.
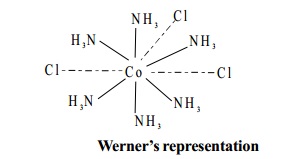
Werner's representation
Werner represented the first member of the series [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 as follows.
In this representation, the primary valency (dotted
lines) are satisfied by the three chloride
ions. The six secondary valencies (solid lines) are satisfied by the six ammonia molecules.
Defects of Werner's theory
Werner's theory describes the structures of many
coordination compounds successfully.
However, it does not explain the magnetic and spectral properties.
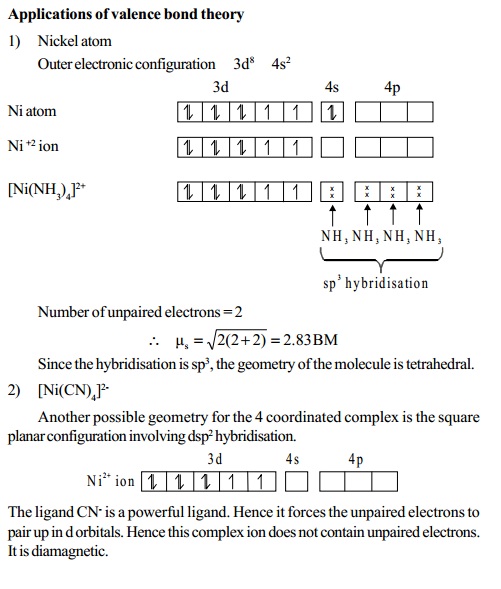
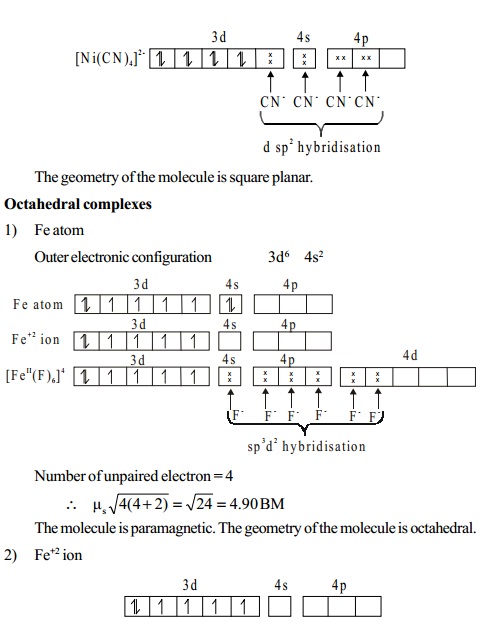
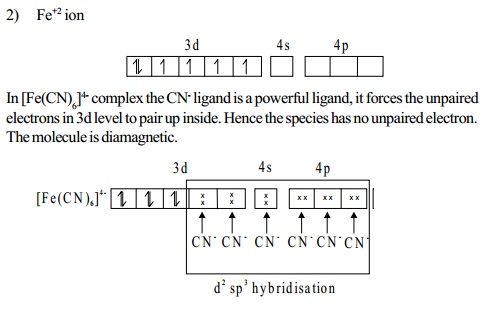
2 Valence bond theory (VB Theory)
Valence bond theory, primarily the work of Linus Pauling
regarded bonding as characterized by the overlap of atomic or hybrid
orbitals of individual atoms.
The postulates of valence bond theory
1.
The central metal
atom/ion makes available a number of vacant orbitals equal to its coordination number.
2. These vacant orbitals form covalent bonds with the ligand
orbitals.
3. A covalent bond is formed by the overlap of a vacant
metal orbital and filled ligand orbitals.
This complete overlap leads to the formation of a metal ligand, s (sigma) bond.
4.
A strong
covalent bond is formed only when the orbitals overlap to the maximum extent. This maximum overlapping is possible only
when the metal vacant orbitals
undergo a process called 'hybridisation'. A hybridised orbital has a better directional characteristics than an
unhybridised one.
The following table gives the coordination number,
orbital hybridisation and spatial
geometry of the more important geometrics.
Coordination
number - Types of hybridization - Geometry
2 -
sp - linear
2 - sp3 - tetrahedral
2 - dsp2 - square planar
2 - d2sp3
- octahedral
2 - sp 3 d 2 - octahedral
Magnetic moment
A species having atleast one unpaired electron, is said
to be paramagnetic.
It is attracted by an external field. The paramagnetic
moment is given by the following spin-only
formula.
ìs = rt(n(n+ 2) )BM
ms = spin-only
magnetic moment
n
= number of unpaired electrons
BM =
Bohrmagneton,theunitwhichexpressesthemagneticmoment.When the species does not contain any unpaired electron, it
is diamagnetic.
Number of unpaired electrons Spin-only moment (BM)
1 root(1(1+ 2)) =
1.73
2 root(2(2 + 2)) =2.83
3 rt(3(3+ 2))= 3.87
4 rt(4(4+2)) = 4.90
5 rt(5(5+ 2))=5.92
Defects of Valence bond theory
Although VB theory was the principal way in which chemist
visualized coordination compounds until
the 1950s, it has fallen into disfavour due to its inability to account for various magnetic, electronic and
spectroscopic properties of these compounds.
Related Topics