Female reproductive part - Gynoecium - Structure of ovule (Megasporangium) | 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Structure of ovule (Megasporangium)
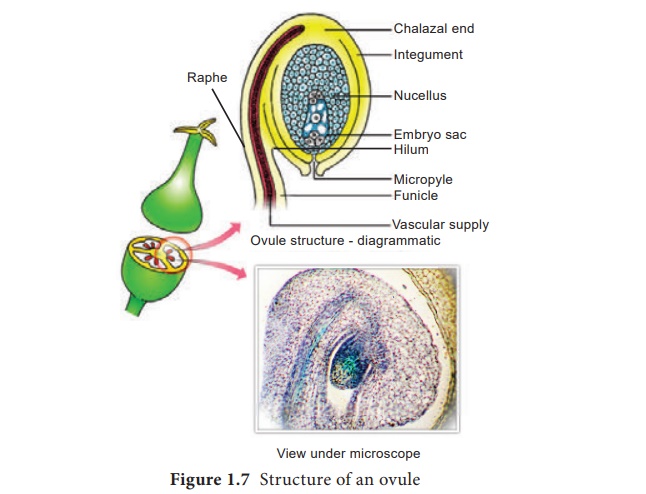
Structure
of ovule(Megasporangium):
Ovule is also called megasporangium and is protected by one or two covering called integuments. A mature ovule consists of a stalk and a body. The stalk or the funiculus (also called funicle) is present at the base and it attaches the ovule to the placenta. The point of attachment of funicle to the body of the ovule is known as hilum. It represents the junction between ovule and funicle. In an inverted ovule, the funicle is adnate to the body of the ovule forming a ridge called raphe. The body of the ovule is made up of a central mass of parenchymatous tissue called nucellus which has large reserve food materials. The nucellus is enveloped by one or two protective coverings called integuments. Integument encloses the nucellus completely except at the top where it is free and forms a pore called micropyle. The ovule with one or two integuments are said to be unitegmic or bitegmic ovules respectively. The basal region of the body of the ovule where the nucellus, the integument and the funicle meet or merge is called as chalaza.
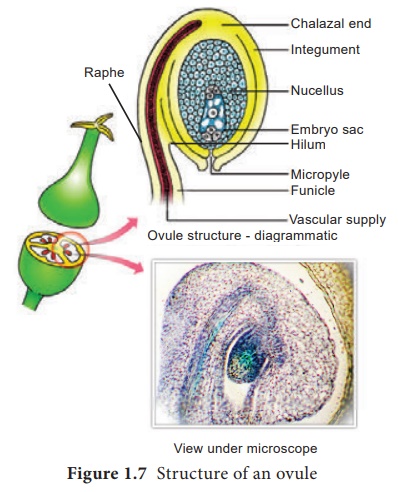
There is a large, oval, sac-like structure in the nucellus toward the micropylar end called embryo sac or female gametophyte. It develops from the functional megaspore formed within the nucellus. In some species(unitegmic tenuinucellate) the inner layer of the integument may become specialized to perform the nutritive function for the embryo sac and is called as endothelium or integumentary tapetum (Example : Asteraceae). There are two types of ovule based on the position of the sporogenous cell. If the sporogenous cell is hypodermal with a single layer of nucellar tissue around it is called tenuinucellate type. Normally tenuinucellate ovules have very small nucellus. Ovules with subhypodermal sporogenous cell is called crassinucellate type. Normally these ovules have fairly large nucellus. Group of cells found at the base of the ovule between the chalaza and embryo sac is called hypostase and the thick -walled cells found above the micropylar end above the embryo sac is called epistase. heT structure of ovule is given in Figure 1.7.
Related Topics