Botany - Reproduction in Plants: Summary | 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Reproduction in Plants: Summary
Summary
Reproduction is one of
the attributes of living things. Lower plants, microbes and animals reproduce
by different methods (fragmentation, gemma, binary fission, budding,
regeneration). Organisms reproduce through asexual and sexual methods. Asexual
methods in angiosperms occur through natural or artificial methods. The natural
methods take place through vegetative propagules or diaspores. Artificial
method of reproduction involves cutting, layering and grafting.
Micropropagation is a modern method used to raise new plants.
Sexual reproduction
includes gametogenesis and fertilization. External fertilization occurs in
lower plants like algae but in higher plants internal fertilization takes
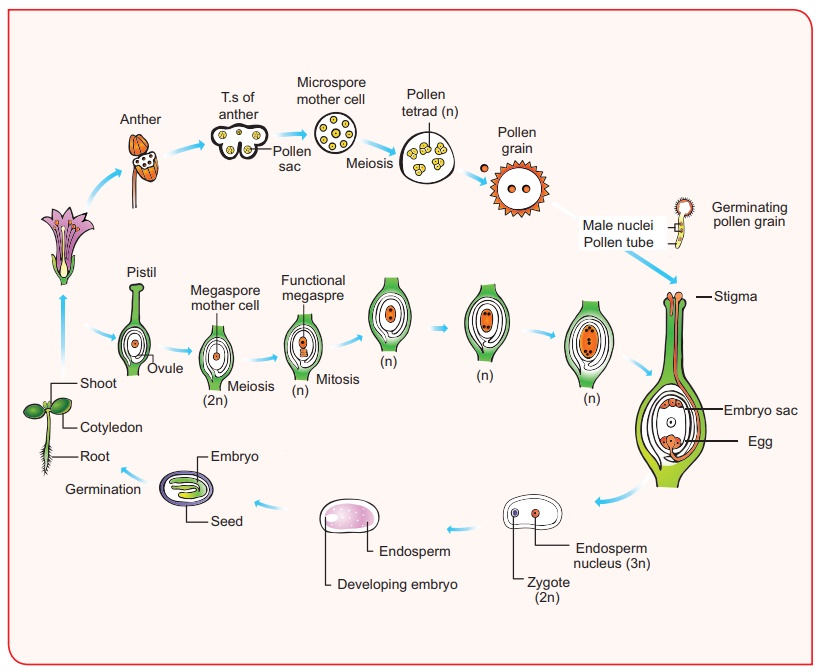
place. A flower is a modified shoot meant for reproduction. Stamen is the male
reproductive part and produces pollen grains. The development of microspore is
called microsporogenesis. The microspore mother cell undergoes meiotic division
to produce four haploid microspores. In majority of Angiosperms the anther is
dithecous and are tetrasporangiate. It possesses epidermis, endothecium, middle
layers and tapetum. The hygroscopic nature of endothecial cell along with thin
walled stomium helps in the dehiscence of anther. Tapetum nourishes the
microspores and also contributes to the wall materials of the pollen grain.
Pollen grain is derived from the microspore and possesses thin inner intine and
thick outer exine. Sporopollenin is present in exine and is resistant to physiological
and biological decomposition. Microspore is the first cell of male gametophyte.
The nucleus of the
microspore divides to form a vegetative nucleus and a generative nucleus. The
generative nucleus divides to form two male nuclei. Gynoecium is the female
reproductive part of a flower and it represents one or more pistils. The ovary
bears ovules which are attached to the placenta. There are six major types of
ovules. The development of megaspore from megaspore mother cell is called
megasporogenesis. A monosporic embryo sac (Polygonum type) possesses
three antipodals in chalazal end, Three cells in the micropylar end
constituting egg apparatus(1 egg and 2 Synergids) and two polar nucleus fused
to form secondary nucleus. Thus, a 7 celled 8 nucleated Embryo sac is present.
The transfer of pollen
grains to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. Self-pollination and
cross-pollination are two types of pollination. Double fertilization and triple
fusion are characteristic features of angiosperms. After fertilization the
ovary transforms into a fruit and the ovule becomes a seed. Endosperm is
triploid in angiosperms and is of three types – Nuclear, cellular, helobial.
Reproduction which doesn’t involve meiosis and syngamy is called apomixis.
Occurrence of more than one embryo in a seed is called polyembryony. Formation
of fruit without the act of fertilization is called parthenocarpy.
Related Topics