Sexual Reproduction in Plants - Self-pollination or Autogamy | 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Self-pollination or Autogamy
Self-pollination or Autogamy
(Greek Auto = self,
gamos = marriage):
According to a majority
of Botanists, the transfer of pollen on the stigma of the same flower is called
self-pollination or Autogamy. Self-pollination is possible only in those
plants which bear bisexual flowers. In order to promote self- pollination the
flowers of the plants have several adaptations or mechanisms. They are:
1. Cleistogamy: In cleistogamy (Greek
Kleisto = closed. Gamos = marriage) flowers never open and expose the
reproductive organs and thus the pollination is carried out within the closed
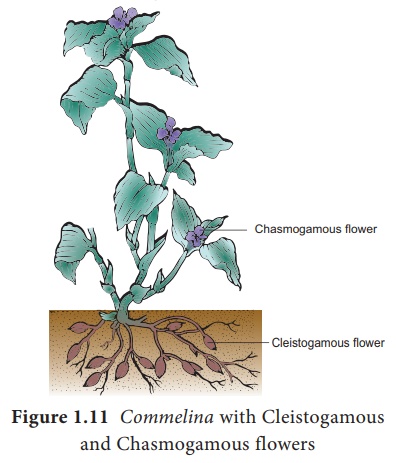
flower. Commelina, Viola, Oxalis are some examples for
cleistogamous flowers. In Commelina benghalensis, two types of
flowers are produced-aerial and underground flowers. The aerial flowers are
brightly coloured, chasmogamous and insect pollinated. The underground flowers
are borne on the subterranean branches of the rhizome that are dull,
cleistogamous and self pollinated and are not depended on pollinators for
pollination.(Figure 1.11).
2. Homogamy: When the stamens and stigma
of a flower mature at the same time it is said to be homogamy. It favours self-pollination
to occur. Example: Mirabilis jalapa, Catharanthus roseus
3. Incomplete dichogamy:
In dichogamous flowers
the stamen and stigma of a flower mature at different time. Sometimes , the
time of maturation of these essential organs overlap so that it becomes
favourable for self-pollination.
Related Topics