Female reproductive part - Gynoecium - Development of Monosporic embryo sac. | 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Development of Monosporic embryo sac.
Development
of Monosporic embryo sac.
To describe the stages
in embryo sac development and organization the simplest monosporic type of
development is given below.
The functional megaspore
is the first cell of the embryo sac or female gametophyte. The megaspore
elongates along micropylar-chalazal axis. The nucleus undergoes a mitotic
division. Wall formation does not follow the nuclear division. A large central
vacuole now appears between the two daughter nuclei. The vacuole expands and
pushes the nuclei towards the opposite poles of the embryo sac. Both the nuclei
divide twice mitotically, forming
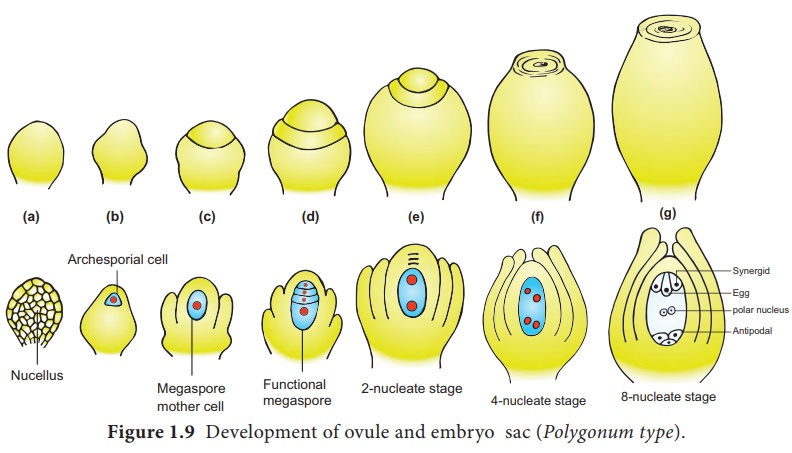
At this stage all the eight nuclei are present in a common cytoplasm
(free nuclear division). After the last nuclear division the cell undergoes
appreciable elongation ,
This is followed by cellular organization of the embryo sac. Of the
four nuclei at the micropylar end of the embryo sac, three organize into an egg
apparatus, the fourth one is left free in the cytoplasm of the central cell
as the upper polar nucleus. Three nuclei of the chalazal end form three antipodal
cells whereas the fourth one functions as the lower polar
nucleus. Depending on the plant the 2 polar nuclei may remain free or
may fuse to form a secondary nucleus (central cell). The egg apparatus
is made up of a central egg cell and two synergids, one on each side of the egg
cell. Synergids secrete chemotropic substances that help to attract the pollen
tube. The special cellular thickening called filiform apparatus of synergids
help in the absorption, conduction of nutrients from the nucellus to embryo
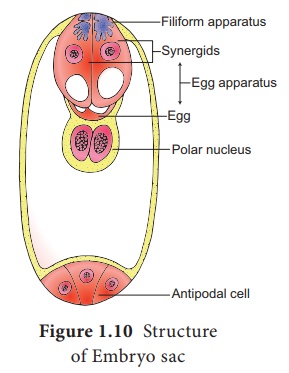
sac. It also guides the pollen tube into the egg. Thus, a 7 celled with 8
nucleated embryo sac is formed. The structure of embryo sac is given in Figure
1.10.
Related Topics