Female reproductive part - Gynoecium - Megasporogenesis | 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 1 : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Megasporogenesis
Megasporogenesis
The process of
development of a megaspore from a megaspore mother cell is called megasporogenesis.
As the ovule develops, a
single hypodermal cell in the nucellus becomes enlarged and functions as archesporium.
In some plants, the archesporial cell may directly function as megaspore mother
cell. In others, it may undergo a transverse division to form outer primary
parietal cell and inner primary sporogenous cell. The parietal cell may remain
undivided or divide by few periclinal and anticlinal divisions to embed the
primary sporogenous cell deep into the nucellus. The primary sporogenous cell
functions as a megaspore mother cell. The megaspore mother cell undergoes
meiotic division to form four haploid megaspores. Based on the number of
megaspores that develop into the Embryo sac, we have three basic types of
development: monosporic, bisporic and tetrasporic. The megaspores
are usually arranged in a linear tetrad. Of the four megaspores formed, usually
the chalazal one is functional and other three megaspores degenerate. The
functional megaspore forms the female gametophyte or embryo sac. This type of
development is called monosporic development (Example: Polygonum).
Of the four megaspores formed if two are involved in Embryo sac formation
the development is called bisporic (Example: Allium). If all the
four megaspores are involved in Embryo sac formation the development is
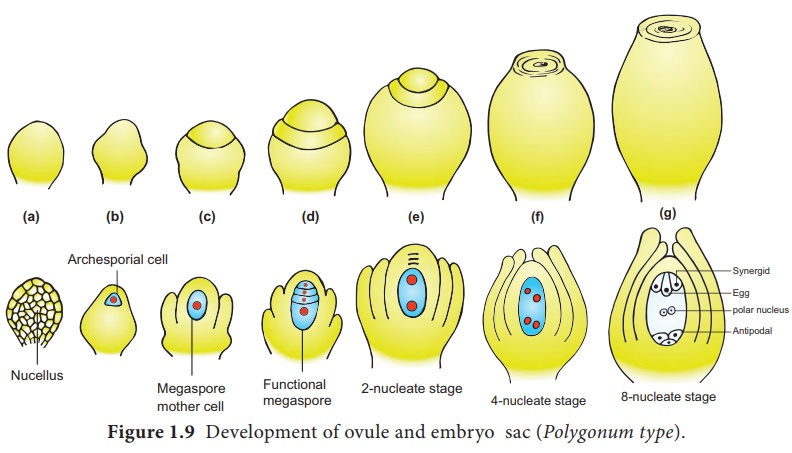
called tetrasporic (Example: Peperomia). An ovule generally has a
single embryo sac. The development of monosporic embryo sac (Polygonum
type) is given in Figure 1.9.
Related Topics