Chapter: Biochemical Pharmacology : Drugs that act on sodium and potassium channels
Some aspects of calcium pharmacology
Some aspects of calcium
pharmacology
Calcium has a dual role in
the regulation of cell function: It carries charge and thus contributes to the
changes of membrane potential in excitable cells, and it acts as a
biochem-ical messenger by directly binding to proteins and modify-ing their
functional state. Proteins directly or indirectly af-fected by calcium are very
diverse and include enzymes, cy-toskeletal proteins, ion channels, and
transcription factors.
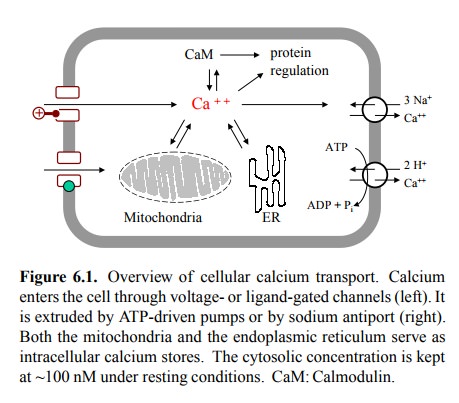
The level of free calcium in
the cytosol is affected by mul-tiple mechanisms of active and passive
transport. These are summarized in Figure 6.1. While the level of calcium in
the cytosol varies in time, it is always much lower than in the extracellular
space, or than in the mitochondria and ER. These two organelles function as
intracellular buffers or reservoirs of calcium. Accordingly, calcium transport
systems operating in both directions exist not only at the cytoplasmic membrane
but also at the mitochondrial (inner) membrane and the ER.
Many of the physiological
effects of Ca++ are mediated by the small protein calmodulin (CaM),
which upon binding of Ca++ changes conformation and binds to
multiple ef-fector proteins, including a variety of protein kinases; pro-tein
phosphorylation is a widely used means of regulation in signal transduction.
Another protein directly activated by Ca++ is the protein
phosphatase calcineurin, which will participate in the reversal of protein
phosphorylation. The spectrum of target proteins for calcium-dependent protein
kinases and phosphatases expressed in a given cell will vary and decide on the
ultimate effects of calcium regulation in the cell.
Calcium-dependent processes
relevant to pharmacological intervention mainly include pace-making in the
heart, and contraction in heart and smooth muscle. These are affected by drugs
that either act on calcium channels directly, or on other receptors that will
have some downstream effect on the cytosolic availability of calcium. Exemples
are the β-and α1-adrenergic receptors (see below).
Related Topics