Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Sodium: Extraction, Physical and Chemical Properties, Uses
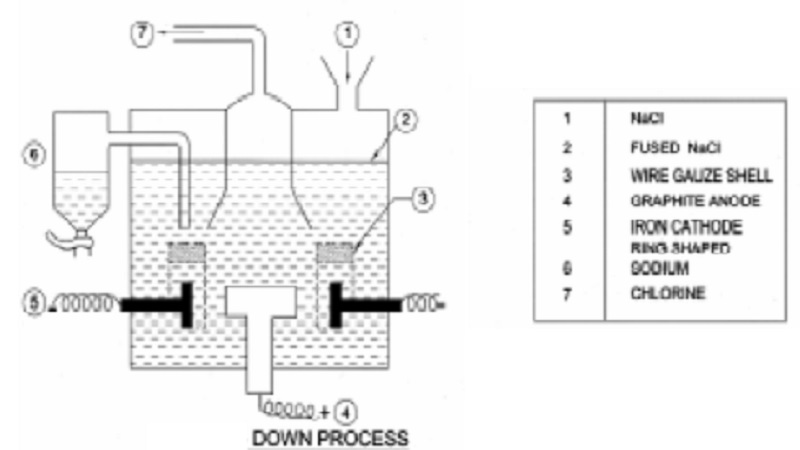
Extraction of Sodium
Down's process : It is now manufactured by electrolysis of fused sodium chloride.
Down's electrolytic cell, consists of an iron box through the bottom of
which rises a circular carbon anode. The anode is surrounded by a ring shaped
iron cathode enclosed in a wire gauze shell which also acts as a partition and
separates the two electrodes.
On
electrolysis, chlorine is liberated at the anode and let out through an exit at
the top. Sodium is liberated at the cathode and remains in the wire-gauze
shell. Level of molten sodium rises and it overflows into a receiver.
2 NaCl -- > 2Na + Cl2
Physical properties
1.
It is a silvery white metal when freshly cut but
is rapidly tarnished in air. It forms tetragonal crystals.
2. It is a soft metal.
3. It is a good conductor of electricity.
4.
It dissolves in liquid ammonia forming an
intense blue solution.
Chemical properties
1) Action of air : In moist air a layer of sodium oxide, hydroxide and carbonate is formed on its surface which loses its lustre.
4Na + O2 -- > 2 Na2O --
(2H2O) -- > 4NaOH --- (2CO2 ) -- >
Na2CO3 + 2H2O
When heated in air, it burns violently to form
the monoxide and the peroxide.
4 Na + O2 -- > 2Na2O
2)
Action of water : It decomposes
water vigorously, liberating hydrogen and forming sodium
hydroxide.
2 Na + 2 H2O
-- > 2 NaOH + H2
3) Action of ammonia: Sodium gives sodamide with ammonia
liberating hydrogen.
2 Na + 2NH3 -- -(570-670K)-- > 2 Na NH2 + H2.
Sodium dissolved in liquid ammonia is used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry.
4.Action of acids: It displaces hydrogen from acids
2 HCl + 2 Na -- > 2 NaCl + H2.
2 Na + 2NH3
-- -(570-670K)-- > 2 Na NH2 + H2.
Sodium
dissolved in liquid ammonia is used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry.
5.Reducing action: Reduces many compounds when heated with them in the absence of air
Al2O3 + 6 Na
--- > 2 Al + 3 Na2O
SiO2 + 4Na -- > Si + 2 Na2O.
Reduces carbondioxide when heated forming carbon and sodium carbonate.
4 Na + 3 CO2 -- > 2 Na2CO3 + C.
6.With Mercury : When heated with mercury, sodium forms an amalgam of varying composition Na2Hg, Na3Hg,
NaHg etc.
Uses
1.
For the preparation of sodium peroxide, sodamide
and sodium cyanide, tetraethyl lead etc.
2.
Sodium amalgam is employed as a reducing agent.
3.
As a deoxidizing agent in the preparation of
light alloys and some rare earth metals from their oxides.
4.
It acts as a catalyst in the polymerisation of
isoprene (C5H3) into artificial rubber.
5.
As a reagent in organic chemistry.
Related Topics