Definition and Rules, Solved Example Problems - Significant Figures | 11th Physics : UNIT 1 : Nature of Physical World and Measurement
Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 1 : Nature of Physical World and Measurement
Significant Figures
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES
Definition
and Rules of Significant Figures
The
digits which tell us the number of units we are reasonably sure of having
counted in making a measurement are called significant figures.
The digits that are known reliably
plus the first uncertain digit are known as significant figures or significant
digits.
For
example, the value of gravitational constant is 6.67 × 10−11 N m2
kg−2. Here the digits 6 and 6 are reliable and certain, while the
digit 7 is uncertain. Thus the measured value has three significant figures.
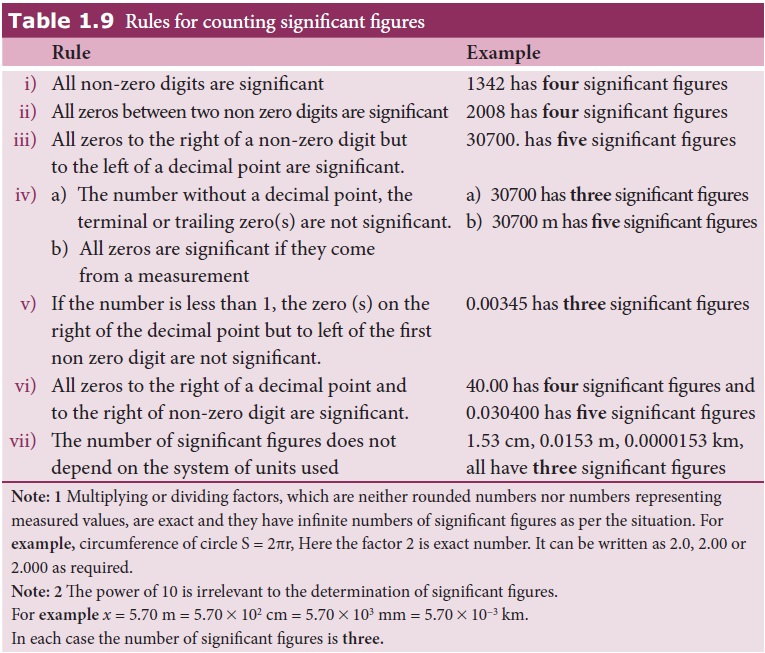
The
rules for counting significant figures are given in Table 1.9.
Example 1.10
State the number of significant figures in the following
i. 600800
ii. 400
iii. 0.007
iv. 5213.0x
v. 2.65 × 1024 m
vi. 0.0006032
Solution
Solution: i) four ii) one iii) one iv) five v) three vi) four
Rounding Off
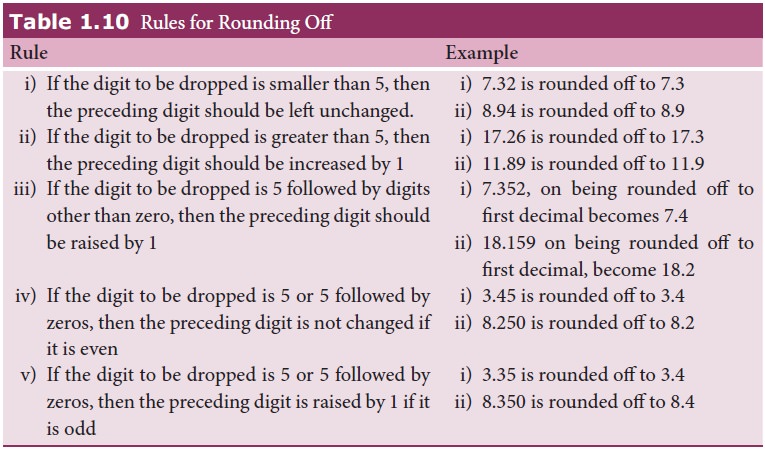
Calculators
are widely used now-a-days to do calculations. The result given by a calculator
has too many figures. In no case should the result have more significant
figures than the figures involved in the data used for calculation. The result
of calculation with numbers containing more than one uncertain digit should be
rounded off. The rules for rounding off are shown in Table 1.10.
Example 1.11
Round off the following numbers as indicated
i) 18.35 up to 3 digits
ii) 19.45 up to 3 digits
iii) 101.55 × 106 up to 4 digits
iv) 248337 up to digits 3 digits
v) 12.653 up to 3 digits.
Solution
i) 18.4 ii) 19.4 iii) 101.6 × 106 iv) 248000 v) 12.7
Arithmetical
Operations with Significant Figures
i. Addition and subtraction
In
addition and subtraction, the final result should retain as many decimal places
as there are in the number with the smallest number of decimal places.
Example:
1)
3.1 + 1.780 + 2.046 = 6.926
Here
the least number of significant digits after the decimal is one. Hence the result
will be 6.9.
2)
12.637 - 2.42 = 10.217
Here
the least number of significant digits after the decimal is two. Hence the
result will be 10.22
ii. Multiplication and Division
In
multiplication or division, the final result should retain as many significant
figures as there are in the original number with smallest number of significant
figures.
Example:
1)
1.21 × 36.72 = 44.4312 = 44.4
Here
the least number of significant digits in the measured values is three. Hence
the result when rounded off to three significant digits is 44.4
2)
36.72 ÷ 1.2 = 30.6 = 31
Here
the least number of significant digits in the measured values is two. Hence the
result when rounded off to significant digit becomes 31.
Related Topics