Nature of Physical World and Measurement | Physics - Short Questions and Answer | 11th Physics : UNIT 1 : Nature of Physical World and Measurement
Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 1 : Nature of Physical World and Measurement
Short Questions and Answer
Nature of Physical World and Measurement | Physics
Short Answer
Questions
1. Briefly explain the
types of physical quantities.
❖
Physical
quantities are classified into two type three are fundamental and derived
quantities.
❖
Fundamental
base quantities are which cannot be expressed in terms of any other physical
quantities. These are length, mass, time electric current, temperature,
luminous intensity and amount of substance.
❖
Quantities
that can be expressed in terms of fundamental quantities are called derived
quantities. For example area, volume, velocity, acceleration, force etc.
2. How will you measure
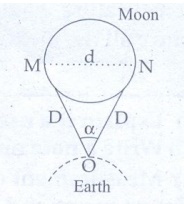
the diameter of the Moon using parallax method?
❖
Once
the distance ‘D’ of a planet is determined the diameter ‘d’ angular size of the
moon can be estimated by parallax method.
❖
Two
diametrically opposite points M and N of moon are viewed through telescope from
a point A on the earth. The angle α between the two directions viewed is
measured. Then by considering MN as arc of length d of a circle with centre at
A and distance D as radius, we can write.
α
= d / D
(or)
d = α D
3. Write the rules for
determining significant figures.
Rule for counting significant
figures
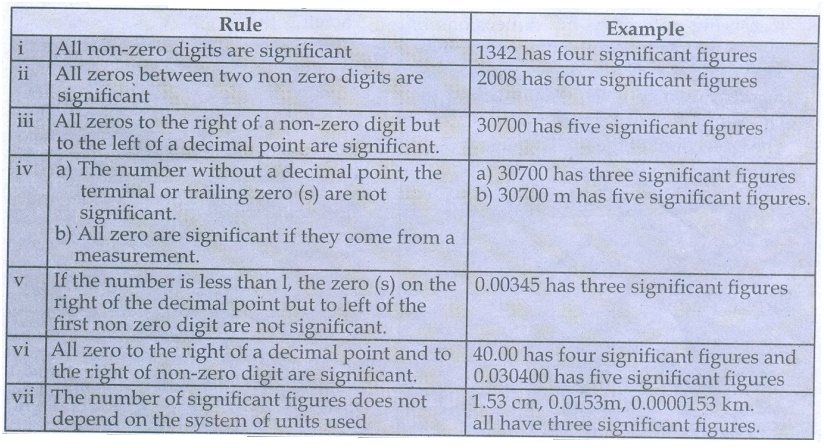
Rule and Example:
i.
All non-zero digits are significant
Example : 1342 has four significant figures
ii.
All zeros between two non zero digits are significant
Example : 2008 has four significant figures
iii.
All zeros to the right of a non-zero digit but to the left of a decimal point
are significant.
Example : 30700 has five significant figures
iv.
a) The number without a decimal point, the terminal or trailing zero (s) are
not significant.
b)
All zero are significant if they come from a measurement.
Example : a) 30700 has three significant figures b) 30700 m
has five significant figures.
v.
If the number is less than 1, the zero (s) on the right of the decimal point
but to left of the first non zero digit are not significant.
Example : 0.00345 has three significant figures
vi.
All zero to the right of a decimal point and to the right of non-zero digit are
significant.
Example : 40.00 has four significant figures and 0.030400
has five significant figures
vii.
The number of significant figures does not depend on the system of units used
Example : 1.53 cm, 0.0153m, 0.0000153 km. all have three
significant figures.
4. What are the
limitations of dimensional analysis?
Limitations of Dimensional
analysis
1.
This method gives no information about the dimensionless constants in the
formula like1, 2………… π, e, etc.
2.
This method cannot decide whether the given quantity is a vector or a scalar.
3.
This method is not suitable to derive relations involving trigonmetric,
exponential and logarithmic functions.
4.
It cannot be applied to an equation involving more than three physical
quantities.
5.
It can only check on whether a physical relation is dimensionally correct but
not the correctness of the relation. For example using dimensional analysis, s
= ut + 1/3at2 is dimensionally correct relation is s = ut ½ at2
5. Define precision and
accuracy. Explain with one example.
Accuracy
is a measure of the closeness of the measured value to the true value.
The
precision of an instrument gives the minimum value that can be measured by it.
If
a measurement is precise, that does not necessarily mean that it is accurate.
How ever if the measurement is consistently accurate, it is also precise.
Example : Let the temperature of a refrigerator repeatedly measured by a thermometer be given as 10.4°C, 10.2°C, 10.3°C, 10.1°C, 10.2°C, 10.1°C, 10.1°C, 10.1°C. However if the real temperature inside the refrigerator is 90C, we say that the thermometer is not accurate but since all the measured value are close to 10°C, hence it is precise.
Related Topics