Chapter: Embedded Systems Design : Basic peripherals
Serial ports
Serial ports
Serial ports are a pin efficient method of communicating between other
devices within an embedded system. With microcontrollers which do not have an
external extension bus, they can provide the only method of adding additional
functionality.
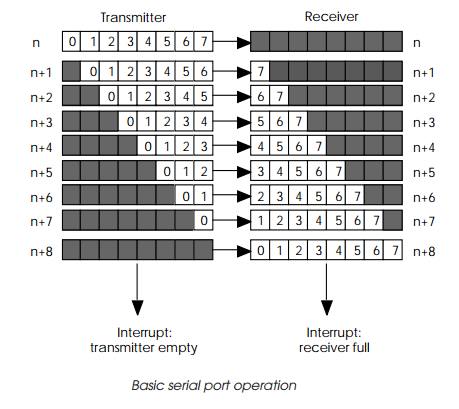
The simplest serial ports are essentially a pair of shift registers that
are connected together with one input (receiver) connected to the output of the
other to create a transmitter. They are clocked together by a common clock and
thus data is transmit-ted from one register to the other. The time taken is
dependent on the clock frequency and the number of bits that are transferred.
The shift registers are normally 8 bits wide. When the transmitter is emptied,
it can be made to generate a local interrupt which can indicate to the
processor that the byte has been transferred and/ or that the next byte should
be loaded into the register. The receiver can also generate an interrupt when
the complete byte is received to indicate that it is ready for reading.
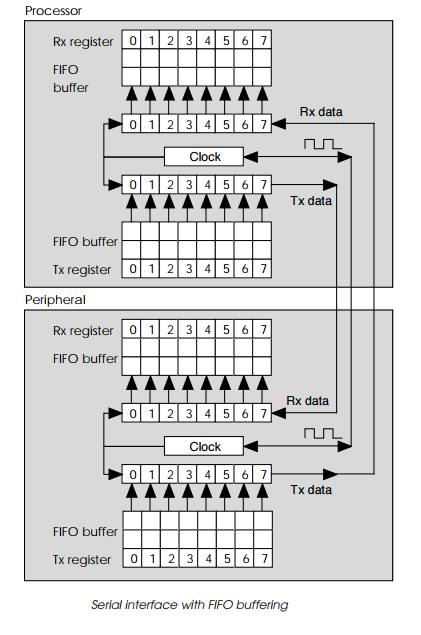
Most serial ports use a FIFO as a buffer so that data is not lost. This can happen if data is transmitted before the preceding byte has been read. With the FIFO buffer, the received byte is transferred to it when the byte is received. This frees up the shift register to receive more bits without losing the data. The FIFO buffer is read to receive the data hence the acronym’s derivation — first in, first out. The reverse can be done for the transmitter so that data can be sent to the transmitter before the previous value has been sent.
The size of the FIFO buffer is important in reducing proces-sor overhead
and increasing the serial port’s throughput as will be explained in more detail
later on. The diagram shows a generic implementation of a serial interface
between a processor and peripheral. It uses a single clock signal which is used
to clock the shift registers in each transmitter and receiver. The shift
registers each have a small FIFO for buffering. The clock signal is shown as
being bidirectional: in practice it can be supplied by one of the devices or by
the device that is transmitting. Obviously care has to be taken to prevent the
clock from being generated by both sides and this mistake is either prevented
by software protocol or through the specification of the interface.
Related Topics