Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Regional Anesthesia & Pain Management: Peripheral Nerve Blocks
Peripheral Nerve Blocks of the Trunk: Superficial Cervical Plexus Block
PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCKS OF THE TRUNK
Superficial Cervical Plexus Block
The superficial cervical plexus block provides cuta-neous analgesia for
surgical procedures on the neck, anterior shoulder, and clavicle. It is helpful
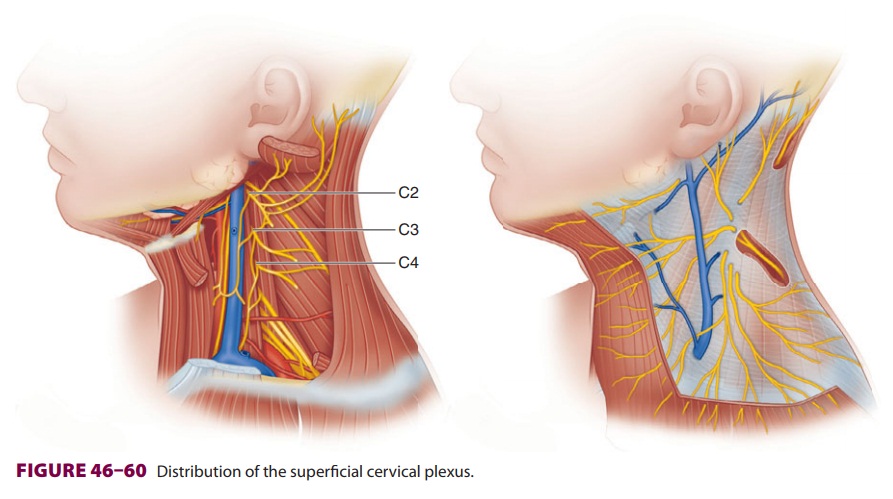
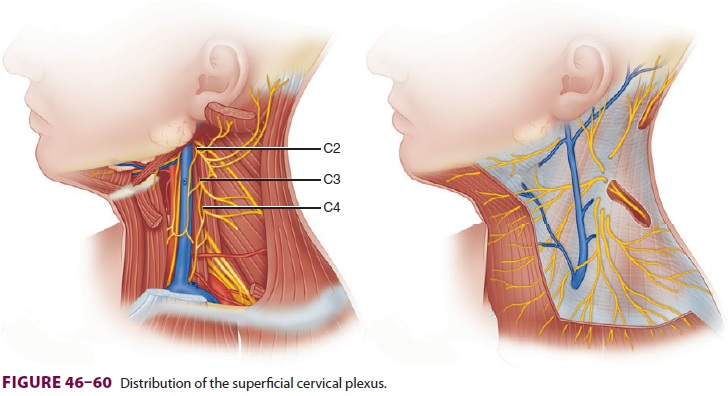
to iden-tify and avoid the external jugular vein. The cervi-cal plexus is
formed from the anterior rami of C1–4, which emerge from the platysma muscle
posterior to the sternocleidomastoid (Figure 46–60). It
supplies sensation to the jaw, neck, occiput, and areas of the chest and
shoulder.
The patient is positioned supine with the head turned away from the side
to be blocked. The ster-nocleidomastoid muscle is identified and its lateral
edge marked. At the junction of the upper and mid-dle thirds, a short (5-cm)
block needle is inserted,
directed cephalad toward the mastoid process, and 5 mL of local
anesthetic is injected in a sub-cutaneous plane. The needle is turned to
advance it in a caudad direction, maintaining a path along the posterior border
of sternocleidomastoid. An additional 5 mL of local anesthetic is infiltrated
subcutaneously.
Related Topics