Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Regional Anesthesia & Pain Management: Peripheral Nerve Blocks
Lower Extremity Peripheral Nerve Blocks: Saphenous Nerve Block
Saphenous Nerve Block
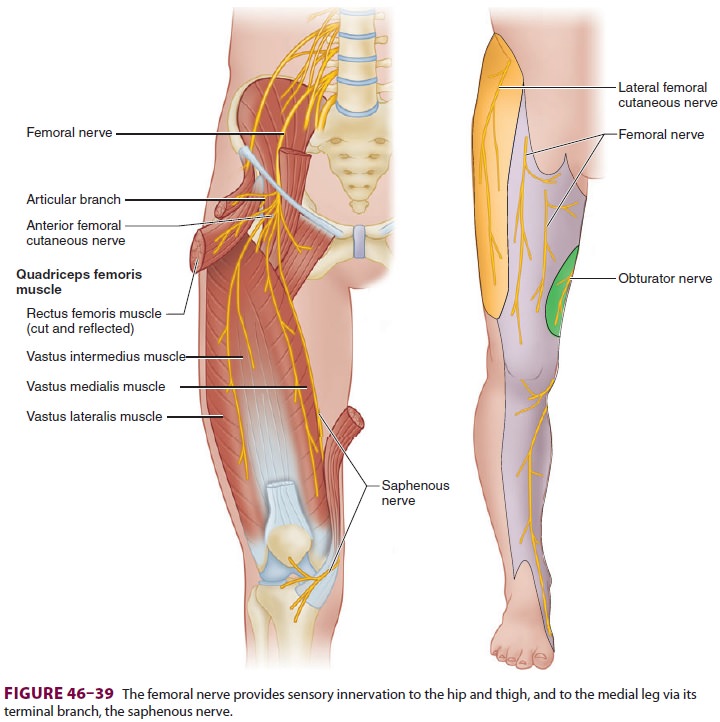
The saphenous nerve is the most medial branch of the femoral nerve and
innervates the skin over the medial leg and the ankle joint (see Figure 46–39).
Therefore, this block is used mainly in conjunc-tion with a sciatic nerve block
to provide complete anesthesia/analgesia below the knee.
A. Trans-Sartorial Technique
The saphenous nerve may be accessed proximal to the knee, just deep to
the sartorius muscle. A high-frequency linear probe is used to identify the
junction between the sartorius, vastus medialis, and adductor muscles in
cross-section just distal to the adductor canal. A long needle is inserted from
medial to lateral (in-plane) or angled cephalad (out-of-plane) and 5–10 mL of
local anesthetic deposited within this fascial plane.
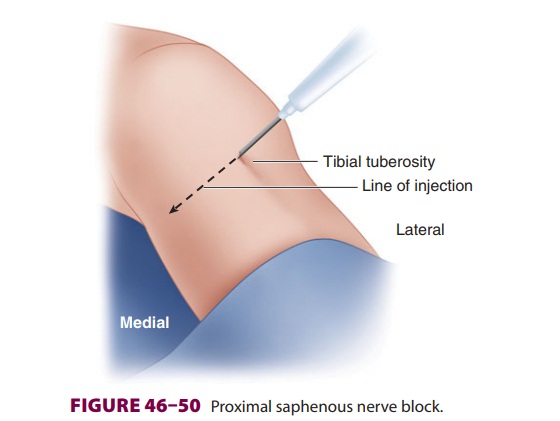
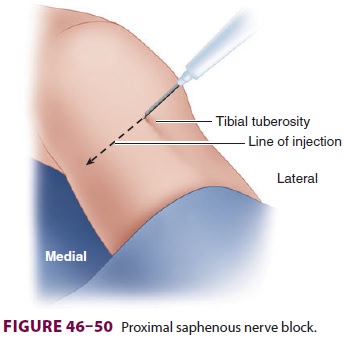
B. Proximal Saphenous Technique
A short block needle is inserted 2 cm distal
to the tibial tuberosity and directed medially, infiltrating 5–10 mL of local
anesthetic as the needle passes toward the posterior aspect of the leg (Figure
46–50). Ultrasound may be used to identify the
saphenous vein near the tibial tuberosity, facilitating a perivas-cular technique with infiltration about the vein.
C. Distal Saphenous Technique
The medial malleolus is identified, infiltrating 5 mL of local
anesthetic in a line running anteriorly around the ankle (see Ankle Block
below).
Related Topics