Mathematics - Ordinary Differential Equations | 12th Maths : UNIT 10 : Ordinary Differential Equations
Chapter: 12th Maths : UNIT 10 : Ordinary Differential Equations
Ordinary Differential Equations
Ordinary
Differential Equations
“Mathematics is the most beautiful and most powerful creation of
the human spirit” - Stefan Banach
Introduction
Motivation and Early Developments
Just we
look at some real life situations where
• the
motion of projectile, rocket, satellite and planets
• the
charge or current in the electric circuit
• the
conduction of heat on a rod or in a slab
• the
vibrations of a wire or membrane etc
are to
be determined. The mathematical formulations of such problems emerge as
differential equations under certain scientific laws. These laws involve
various rates of change (derivatives) of one or more quantities with respect to
other quantities. Thus the scientific laws manifest as mathematical equations
involving derivatives, viz. differential equations.
Differential
Equations emanate from the problems in geometry, mechanics, physics, chemistry,
and engineering studies. We have studied about “rates” in our early classes. This
is also known as instantaneous rate of change which is denoted as dy/dx.
We give
below some relations between the rate of change and unknown functions that
occur in real life situations.
(a) The
rate of change of y with respect to x is directly proportional to y :
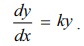
(b) The
rate of change of y with respect to x is directly proportional to the
product of y2 and x :
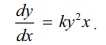
(c) The
rate of change of y with respect to x is inversely proportional to y :
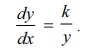
(d) The
rate of change of y with respect to x is directly proportional to y2 and inversely proportional
to √x :
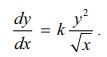
A
differential equation is an equation in which some derivatives of the unknown
function occur.
In many
cases the independent variable is taken to be time.
In order
to apply mathematical methods to a physical or “real life” problem, we must
formulate the problem in mathematical terms; that is, we must construct a
mathematical model for the problem. Many physical problems concern
relationships between changing quantities. Since rates of change are
represented mathematically by derivatives, mathematical models often involve
equations relating to an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives.
Such equations are differential equations. They are of basic significance in
science and engineering since many physical laws as well as relations are
modelled in the form of differential equations. Differential equations are much
useful in describing mathematical models involving population growth or
radio-active decay. The study of biological sciences and economics is
incomplete without the application of differential equations.

The
subject of differential
equations was invented along with calculus by Newton and Leibniz in order to
solve problems in geometry and physics. It played a crucial part in the
development of Newtonian physics by the Bernoulli family, Euler, and others.
Some of the applications of differential equations in our daily life are found
in mobile phones, motor cars, air flights, weather forecast, internet, health
care, or in many other daily activities.
In this
chapter, we introduce and discuss the first order ordinary differential equations
and some methods to find their solutions.
Learning Objectives
Upon
completion of this chapter, students will be able to
• classify
differential equations
• construct
differential equations
• find
the order and degree of the differential equations
• solve
differential equation using the methods of variables separable, substitution,
integrating factor
• apply
differential equation in real life problems
Related Topics