Chapter: Human Neuroanatomy(Fundamental and Clinical): Introduction to Neuroanatomy
Neural Crest
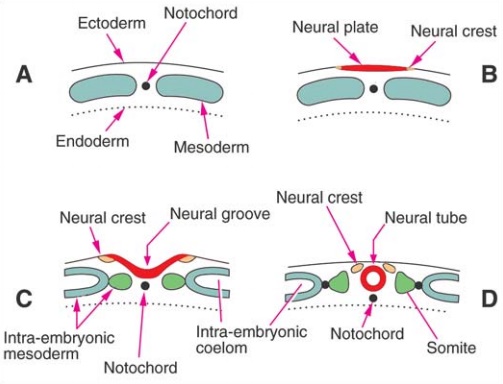
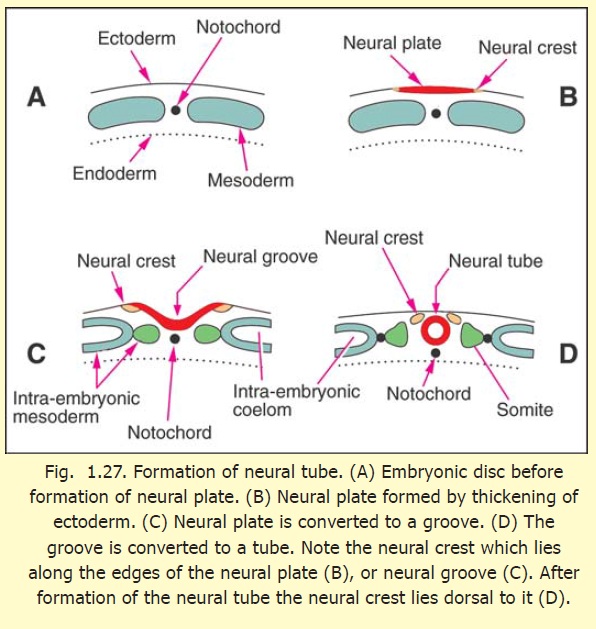
The Neural Crest
At the time when the neural plate is being formed, some cells at the junction between the neural plate and the rest of the ectoderm become specialised (on either side) to form the primordia of the neural crest (Figs. 1.27 B, C). With the separation of the neural tube from the surface ectoderm, the cells of the neural crest appear as groups of cells lying along the dorsolateral sides of the neural tube (Fig. 1.27D). The neural crest cells soon become free (by losing the property of cell to cell adhesiveness). They migrate to distant places throughout the body. In subsequent development, several important structures are derived from the neural crest. These include some neurons of sensory and autonomic ganglia, Schwann cells, and possibly the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. Many other derivatives of the neural crest are recognised in widespread tissues.
Related Topics