Chapter: Human Neuroanatomy(Fundamental and Clinical): Introduction to Neuroanatomy
Nodes of Ranvier
Nodes of Ranvier
We have seen that the myelin sheath is in the form of segments separated at nodesof Ranvier. We have also noted that thepart of the nerve fibre between two such nodes is called the internode. The length of the internode is greater in thicker fibres and shorter in thinner ones. It varies from 150 to 1500 μm.
The nerve fibres within a nerve frequently branch. When they do so the bifurcation always lies at a node.
The nodes of Ranvier have great physiological importance. When an impulse travels down a nerve fibre it does not proceed uniformly along the length of the axis cylinder, but jumps from one node to the next. This is called saltatoryconduction.
(In unmyelinated neurons the impulse travels along the axolemma. Such conduction is much slower than saltatory conduction and consumes more energy).
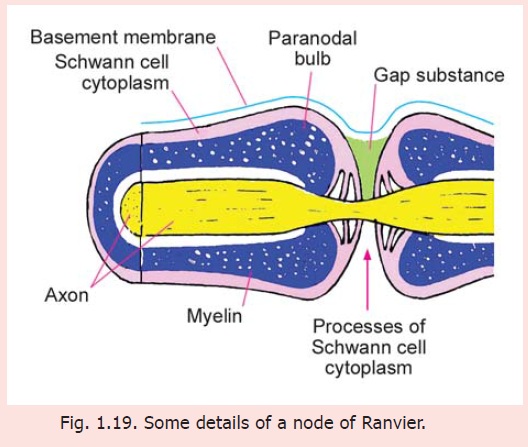
EM studies reveal several interesting details about the nodes of Ranvier (Fig. 1.19). Immediately next to a node the myelin sheath shows an expansion called the paranodal bulb. There are longitudinal furrows on the surface of the paranodal bulb. These furrows are filled in by Schwann cell cytoplasm containing many mitochondria. Finger-like processes of this cytoplasm extend towards the naked part of the axon and come in contact with it. These processes interdigitate with those from neighbouring Schwann cells. In the intervals between these processes the axon is covered by a gap substance that plays a role in regulating the flow of the nerve impulse by influencing the passage of ions into, and out of, the axon.
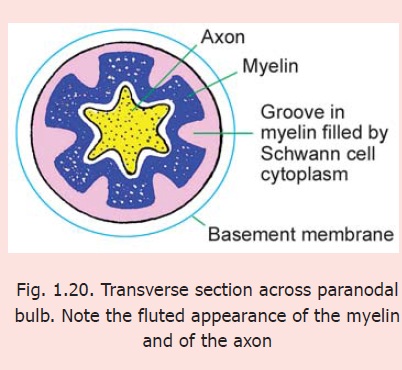
At a node of Ranvier the axon itself is much thinner than in the internode. The part of the axon passing through the paranodal bulb shows infoldings of its axolemma (cell membrane) that correspond to the grooves on the surface of the paranodal bulb (Fig. 1.20).
Related Topics