Chapter: Human Neuroanatomy(Fundamental and Clinical): Introduction to Neuroanatomy
Sex chromatin in neurons
Sex chromatin in neurons
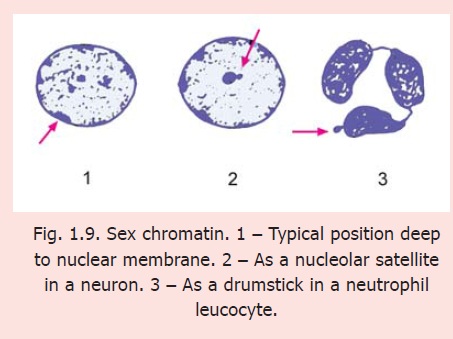
Each cell of a human male has 44+X+Y chromosomes; and each cell of a female has 44+X+X chromosomes. Of the two X-chromosomes in a female only one is functionally active. The other (inactive) X-chromosome forms a mass of dark staining hetero-chromatin that can be identified in suitable preparations and can be useful in determining whether a particular tissue belongs to a male or a female. Because of this association with sex this mass of hetero-chromatin is called the sexchromatin. It is also called a Barr body after the name of the scientist who discovered it. In most cells the sex chromatin lies just under the nuclear membrane (Fig. 1.9). In some cells the sex chromatin occupies a different position from that described above. In neurons it forms a rounded mass lying very close to the nucleolus and is, therefore, called a nucleolar satellite. In neutrophil leucocytes it may appear as an isolated round mass attached to the rest of the nucleus by a narrow band, thus resembling the appearance of a drumstick.
Related Topics