Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Molecular orbital energy level diagrams -Hydrogen, Hypothetical, Nitrogen, Oxygen
Molecular
orbital energy level diagrams of certain diatomic Homo nuclear molecules and molecular ions
The filling of molecular orbitals is governed by the
following principles.
(i)Aufbau principle
(ii)Pauli's exclusion principle and
(iii)Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity. Now, let us consider some examples of homo nuclear
diatomic molecules.
1.
Hydrogen molecule, H2. It is formed by the combination of two hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom in the ground
state has one electron in 1s orbital.
Therefore, in all there are two electrons in hydrogen molecule which are present in lower most s1s molecular orbital.
According to Pauli's exclusion principle,
these two electrons should have opposite spins.
The molecular orbital electronic configuration of
hydrogen molecule is (s1s)2.
The
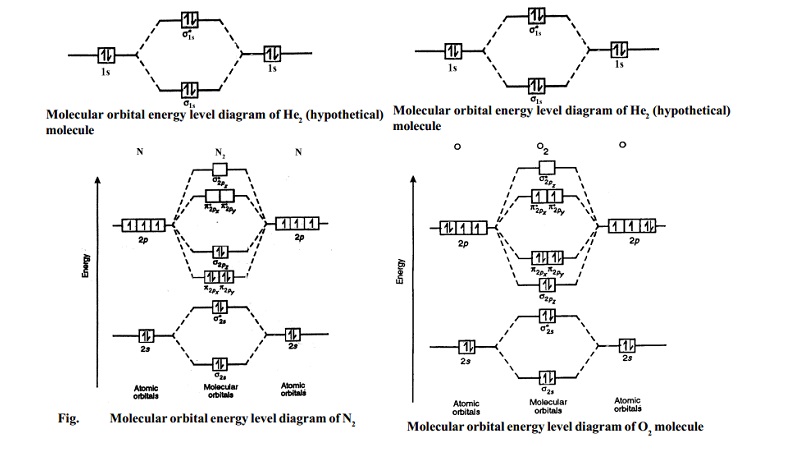
molecular orbital energy level diagram of H2 molecule is given in Fig..
The bond order of H2 molecule can be calculated as follows.
Here, Nb = 2 and Na = 0
Bond order = (Nb - Na) /2 = 2-0/2 = 2
i.
Nature of
bond : This means that the two hydrogen atoms in a molecule
of hydrogen are bonded by a single
covalent bond.
ii.
Diamagnetic
character : Since no unpaired
electron is present in hydrogen molecule,
it is diamagnetic in nature.
2.
Diatomic helium molecule, He2 (Hypothetical).
The electronic configuration of helium (Z =
2) in the ground state is 1s2. As each helium atom contains two electrons, there will be four
electrons in He2 molecule. Keeping in view the Aufbau principle and Pauli's
exclusion principle its electronic configuration would be as follows.
He2 : (s1s)2 (s*1s)2.
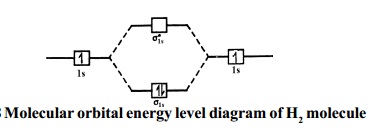
The molecular orbital energy
level diagram of He2 (hypothetical) is given
in Fig.
Here, Nb = 2 and Na = 2
Bond order = Nb - Na / 2 = 2 - 2 / 2 = 0.
As the bond order for He2 comes out to be zero, this molecule does not exist.
3. Nitrogen molecule (N2). The electronic configuration of nitrogen (Z=7) in the ground state is 1s2 2s2 2p1x 2p1y 2p1z . Therefore, the total number of electrons present in nitrogen molecule (N2) is 14. These 14 electrons
can be accommodated in the various
molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy.
N2 : KK(s2s )2 (s*2s )2 (P2px )2 (P2py )2 (s2pz )2
Here (s1s )2 (s*1s )2 part of
the configuration is abbreviated as KK, which denotes the K shells of the two atoms. In calculating bond order, we
can ignore KK, as it includes two bonding and two antibonding electrons.
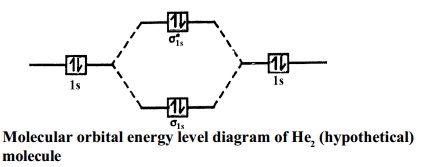
The molecular orbital energy level diagram of N2 is given in Fig..
The bond order of N2 can be calculated as follows.
Here, Nb = 8 and Na = 2
∴ Bond
order = ( Nb - Na ) / 2 =( 8 - 2) /2 =
3.
i.
Nature of
bond : A bond order of 3 means that
a triple bond is present in a molecule of
nitrogen.
ii.
Diamagnetic
nature : Since all the electrons in
nitrogen are paired, it is diamagnetic
in nature.
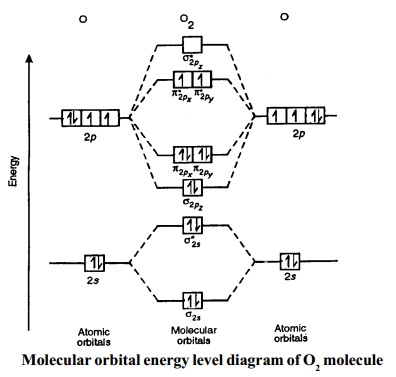
4. Oxygen molecule, O2. The electronic configuration of oxygen (Z = 8) in the ground state is 1s22s22p4. Each oxygen atom has 8 electrons,
hence, in O2 molecule there are 16 electrons. Therefore, the
electronic configuration of O2 is as follows.
O2 : KK(s2s )2 (s*2s )2 (s2pz )2 (P2px )2 = (P2py )2 (P*2px )1 = (P*2py )1
Here (s1s )2 (s*1s )2 part of
the configuration is abbreviated as KK.
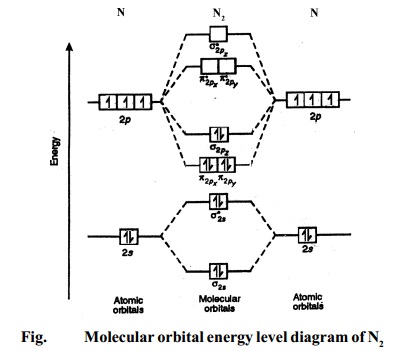
The molecular
orbital energy level diagram of O2 molecule is
given in Fig.
Bond order =
(Nb - Na ) / 2 =( 8 - 4) / 2 = 2.
Related Topics