Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals
Molecular Orbital Theory : Energy level diagram for molecular
orbitals
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY
Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and
Mullikan in 1932.
This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in
molecules, atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in
molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals. A brief outline
of this theory is given below:
(i) In a molecule, electrons are present in new orbitals called
molecular orbitals. (ii) Molecular orbitals are formed by combination of
atomic orbitals of equal energies (in case of homonuclear molecules) or of
comparable energies (in case of heteronuclear molecules).
(iii) The number of molecular orbitals formed is equal to the number of
atomic orbitals undergoing combination.
(iv) Two atomic orbitals can combine to form two molecular orbitals. One
of
these two molecular orbitals one has a lower energy and the other has a
higher energy. The molecular orbital with lower energy is
called bonding molecular orbital and the other
with higher energy is called anti bonding molecular orbital.
(v) The shapes of molecular orbitals depend upon the shapes
of combining atomic orbitals.
(vi) The bonding molecular orbitals are represented by s (sigma), p (pi), d (delta) and the antibonding molecular orbitals are represented by s*, p*, d*.
(vii) The molecular orbitals are filled in the increasing order of
their energies, starting with orbital of least energy. (Aufbau principle).
(viii) A molecular orbital can accommodate only two electrons and these
two electrons must have opposite spins. (Paul's exclusion
principle).
(ix) While filling molecular orbitals of equal energy, pairing of
electrons does not take place until all such molecular orbitals are
singly filled with electrons having parallel spins.
(Hund's rule).
Energy level
diagram for molecular orbitals
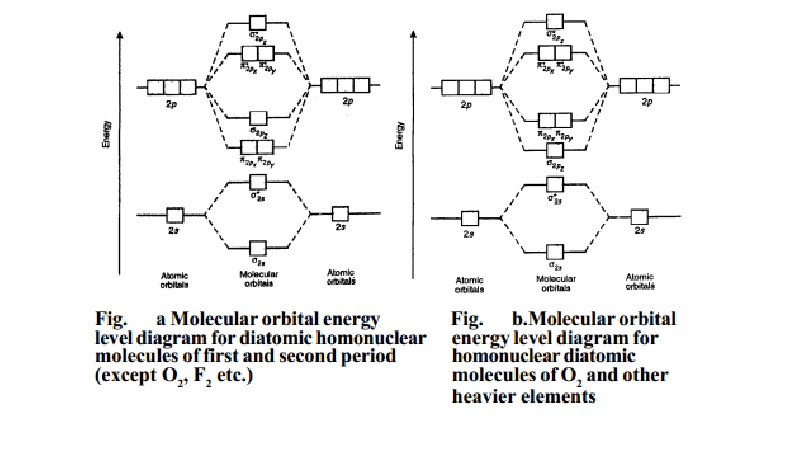
In case of homonuclear diatomic molecules, combination of
two 1s atomic orbitals of participating atoms give rise to two new
molecular orbitals designated as s1s and s*1s. In the same manner the 2s and three 2p-orbitals of each
atom i.e., eight atomic orbitals can give rise to eight new
molecular orbitals viz.,
s2s , s2s , P 2px , P *2px , P 2py , P *2py , s2pz , s2pz .
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
Energy levels of these molecular orbitals have been
determined experimentally by spectroscopic studies.The order of
increasing energy in case of the diatomic homonuclear
molecules of first and second period of the periodic table is as given below:
s1s < s*1s < s2s < s*2s < P2px = P 2py < s2pz < P *2px = P
*2py < s*2pz
This order of energies of various molecular orbitals is
valid for molecules or ions like, H2, H2+, He2+, He2 (hypothetical), Li2, Be2(hypothetical), B2, C2 and N2molecules.
This energy diagram for the molecular orbitals is shown in Fig.1 However, experimental evidence for oxygen and heavier diatomic
molecules have shown that above sequence of energy levels of MOs is not correct. In
case of these
elements, the order of energy levels of s2pz , P 2pxand P 2py is reversed i.e., s2pz has lesser energy than P 2px or P 2py . Thus, the order of increasing
energy of MOs for
these molecules is as follows.
s1s < s*1s < s2s < s*2s < s 2pz < P 2px = P 2py < P *2px = P *2py < s*2pz 1s
This order of energies of various MOs is valid for
molecules or ions like O2, O (super oxide ion), O22-(peroxide ion), F2 and Ne2 (hypothetical). This energy level diagram for MOs is shown in Fig. (b).
Related Topics