Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Classification of Organic Compounds: open chain, cyclic compounds
Classification of Organic Compounds : open chain and cyclic compounds
The
organic compounds are classified into two main types, namely.
(1) Open -
chain or acyclic compounds or aliphatic compounds
The open chain or acyclic compounds are those in which carbon atoms are
linked to each other either in linear or branched fashion such that the
molecule is having open chain structure. These compounds are also called aliphatic
compounds (Greek word : aliphar meaning fat).
Examples
CH3 - CH3
- CH3 propane
(2) Closed
chain or cyclic compounds
Organic compounds with closed chain of atoms are called closed chain
compounds or ring compounds.
These compounds are further classified into
(a)
Homocyclic or carbocyclic compounds
(b)Heterocyclic compounds
(a)
Homocyclic compounds :
In these compounds the ring structure is made
up of only carbon atoms.
These compounds are further classified into
i.Aromatic compounds and
ii. Alicyclic compounds
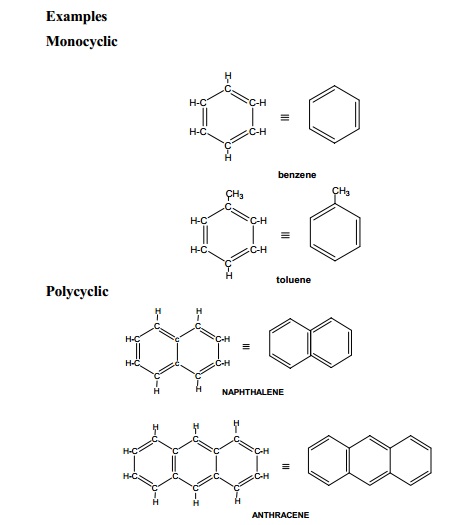
(i) Aromatic compounds (Benzenoid) :
Compounds containing one or more benzene rings in their structure are
classified as aromatic benzenoid compounds. Most of these compounds have
pleasant odour (Greek : Aroma - sweet smell).
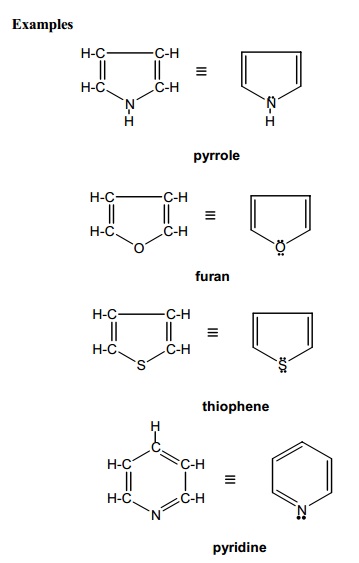
(b) Heterocyclic
compounds (Non - benzenoid aromatic) : Cyclic compounds
in which the ring atoms are made up of hetero atoms like nitrogen, oxygen
and sulphur in addition to carbon atoms are called heterocyclic compounds.
The above compounds are aromatic non-benzenoid compounds.
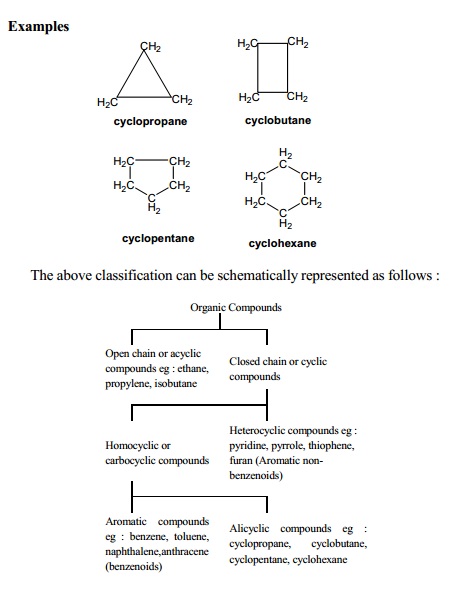
(ii) Alicyclic
compounds : Cyclic compounds with ring structure containing
only carbon atoms are called alicyclic or carbocyclic compounds. Though these
compounds possess a ring structure, they behave more like aliphatic compounds.
Characteristics
of organic compounds
All organic compounds have the following characteristic properties
1. Many organic compounds are inflammable
2.
They are mostly covalent compounds
3.
They are generally soluble in non - polar
solvents like carbon tetrachloride, benzene etc.
4. They have generally low boiling point and melting point.
5.
They exhibit isomerism
Homologous
series
A group or class of organic compounds related to
each other by a general molecular formula contributes homologous series.
Characteristics
of homologous series
Homologous series have the following characteristics :
(1)
All members of a series contain same elements
and the same functional groups.
(2)
All the members of a homologous series can be
represented by a general formula
Examples
Alkanes CnH2n+2
Alkenes CnH2n
Alkynes CnH2n-2
(3)
All the members of a homologous series can be
prepared by similar methods.
(4)
All members of a homologous series usually
undergo similar chemical reactions.
(5)
Successive members in a series differ by a -CH2
group
(6)
The physical properties of the members of a
homologous series vary in a regular way down the series. For example, boiling
point, melting point and density of the alkane series vary in a regular way
with increasing number of carbon atoms.
Related Topics