Communicable Diseases - Mode of Transmission | 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Mode of Transmission
Mode of Transmission
Infectious diseases are transmitted from person to person by
direct or indirect contact. Certain types of viruses, bacteria, parasites, and
fungi can cause infectious disease. Malaria, measles, and respiratory illnesses
are examples of infectious diseases.
Susceptible Host - A person who lacks resistance to a particular
pathogenic agent to prevent disease if or when exposed.
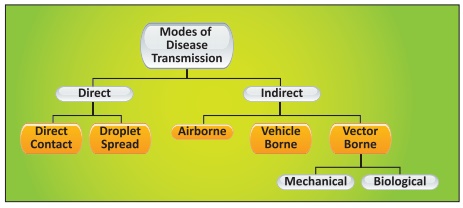
I. Direct Transmission
1. Direct Contact - Infection may be transmitted directly
from skin to skin, mucosa to mucosa, mucosa to skin of others or same person.
Example: skin-to-skin contact as by touching, kissing or sexual intercourse.
Diseases transmitted - STD and AIDS, leprosy, leptospirosis, skin and eye
infections.
2. Droplet infection -This is direct projection of a spray of
droplets of salaiva and nasopharyngeal secretions (airborne droplets of saliva
or sputum) containing infectious organisms. The spray of droplets during
coughing and sneezing can spread an infectious disease.
3. Contact with soil - The disease agent may be acquired by
direct exposure of susceptible tissue to the disease agent in soil, compost or
decaying vegetable matter. Examples: hookworm larvae, tetanus, mycosis etc.
4. Inoculation into skin or mucosa - Rabies virus by dog
bite, Hep. B virus through contaminated needles and syringes etc.
5. Transplacental (or vertical) transmission - TORCH agents - (Toxoplasma Gondii, Rubella virus, Cytomegalo virus, and Herpes virus). Varicella virus, Syphilis, Hepatitis B, Coxsackie B and AIDS. Some of the non-living agents (e.g., thalidomide, diethylstilbestrol) can also be transmitted vertically (mother to child) which will affect the embryo and causes malformations in the foetus.
2. Indirect Transmission
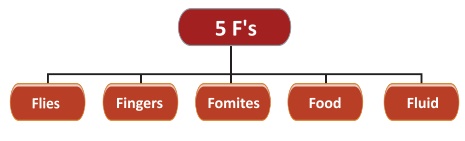
This embraces a variety of mechanisms including the traditional 5
F's, such as
1. Vehicle-borne - An indirect transmission of an infectious
agent that occurs when a vehicle. (or formites) touches a persons body or is
ingested
2. Vector - borne - Vector is defined as an arthropod or
any living carrier that transports an infectious agent to a susceptible
individual. Infectious agents are transmitted by insects, especially those that
suck blood. These include mosquitoes, fleas, and ticks. The insects become
infected when they feed on infected hosts, such as birds, animals, and humans.
The disease is transmitted when the insect bites a new host. Eg. Malaria, West Nile
virus, and Lyme disease are all spread this way.
3.
Airborne - An airborne disease is
any disease that is caused by pathogens that can be transmitted through
air. Some infectious agents can travel long distances and remain suspended in
the air for an extended period of time. Diseases spread by droplet include
tuberculosis, measles, Q fever, and Respiratory infections.
4.
Fomite - borne - Fomites are inanimate
articles or substances other than water or food contaminated by the
infectious discharges from a patient and capable of harbouring and transferring
infectious agent to a healthy person. Fomites includes soiled clothes, toys,
towels, linen, cups, spoons, pencils, books, surgical dressing, etc., Diseases
transmitted by fomites are typhoid, diphtheria, and skin infections.
5. Unclean hands and fingers - Hands are the most common medium by
whichpathogenic agents are transferred to food from the skin, nose, bowel,
etc., as well as from other food.
Chain of Disease Transmission
The six factors involved in the chain of disease transmission are
Related Topics