Introduction, Terminology - Communicable Diseases | 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Communicable Diseases
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
Introduction
Infections due to living organisms are called communicable
diseases. They spread from person to person, or sometimes from animals to
people. They occur at all ages but are most serious in childhood and they are
preventable to a great extent. In developed countries, communicable diseases have
been prevented. But in India it is going through a period of transition, both
epidemiological and demographically. Infectious diseases are still persisting
as major health problems in spite of having National programmes for the control
of many diseases.
Terminology
·
Infection:
The entry and
development or multiplication of an infectious agent in the body of
human being or animals.
·
Contamination:
The presence of
infectious agent on a body surface or in clothes, beddings, toys,
surgical instruments or dressings or other inanimate articles or substances
including water, milk and food.
·
Infestation:
For persons or animals
the lodgment, development and reproduction of arthropods on the surface
of the body or in the clothing (e.g) lice, itch mite.
·
Host:
A person or animal
including birds and arthropods that affords subsistence or lodgment to
an infectious agent under natural condition.
·
Communicable
diseases: An
illness due to specific infectious agent or its toxic products capable
of being directly or indirectly transmitted from man to man, animal to animal
or from the environment to man or animal.
·
Epidemic:
The unusual occurrence
or sudden outbreak of disease in a community or region.
·
Endemic:
It refers to the constant
presence of a disease or infections agent within a given geographic area
or population group.
·
Sporadic:
The word sporadic means
scattered about. The diseases are so few and separated widely in space.
·
Pandemic:
An epidemic usually
affecting a large proportion of the population, occurring over a wide
geographic area such as a section of a nation, the entire nation, a continent
or world (eg.) influenza pandemic
·
Zoonosis:
An infection
transmissible under natural conditions from vertebrate animals to man.
Eg. Rabies, plague
·
Eradication:
Termination of all
transmission of infection through surveillance.
Carriers
A carrier is defined as “an infected person or animal that
harbours a specific infectious agent in the absence of clinical manifestation
and serves as a potential source of infection to others.
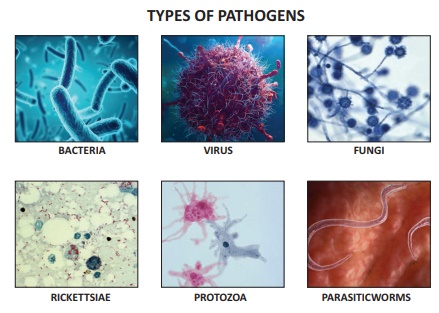
Definition
Communicable Disease - “An illness due to a specific
infectious agent or its toxic products capable of being directly or indirectly
transmitted from man to man, animal to animal, or from the environment (through
air, dust, soil, water, food, etc.) to man or animal.
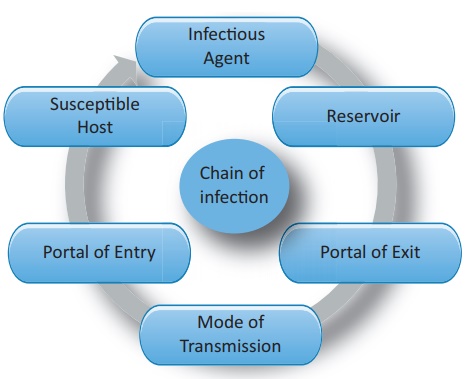
Chain of Infection
Related Topics