Definition, Causative organism, Complications, Clinical manifestations, Preventive measures - Chickenpox (Varicella) | 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Chickenpox (Varicella)
Diseases Transmitted Through Air
Chickenpox (Varicella)
Definition - Chickenpox or varicella is an acute highly infectious
disease caused by varicella zooster
Causative organism
Varicella zoster
Mode of transmission - Droplet nuclei Incubation period -
About 10 -21 days
Complications (Children and Adults)
·
Haemorrhages
·
Pneumonia
·
Encephalitis
·
Acute cerebellar ataxia
The control measures are notifications isolation of cases for
about 6 days after onset of rashes and disinfection of articles soiled by nose
and throat discharges.
Clinical manifestations
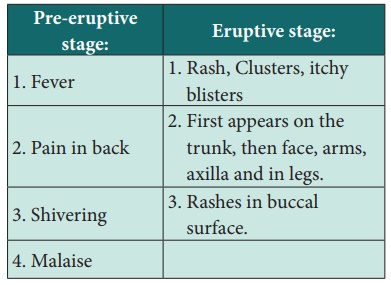
Preventive measures
1. Varicella zooster immunoglobulin : Varicella
zooster immunoglobulin given within 72 hours of exposure has been recommended
for prevention of chicken pox.
2. Vaccines : The live attenuated varicella virus vaccine is safe and
currently recommended for children between 12-18 months of age who have not had
chicken pox.
Medication
·
Anti – pyretic
Anti viral drugs
Related Topics