Definition, Clinical manifestations, Causative Organism, Control measures, Treatment, Complications - Acute Diarrheal Diseases | 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Communicable Diseases
Acute Diarrheal Diseases
Acute Diarrheal Diseases
Definition
According to WHO Acute diarrhea is defined as an abnormally
frequent discharge of semisolid or fluid faecal matter from the bowel, lasting
less than the 14 days by WHO.
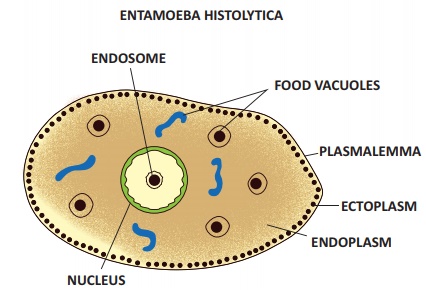
Causative Organism
Bacteria: Escherichia coli, Shigella, salmonella etc.,
Virus: Rota virus, adenovirus etc.
Parasites: Endamoeba hystelytica, Giardia lamblin etc.
Mode Of Transmission - Direct transmission - Faeco – oral route
Incubation Period - Few Hour to one day.
Clinical Manifestation
·
Sunken eyes
·
Tachycardia
·
Hypotension
·
Irritable and
restlessness
·
Pallor
·
Rapid respiration
·
Sudden collapse if not
treated properly
·
Stools loose and fluid
in consistency, greenish or yellow green in colour, may contain mucus or blood.
·
Vomiting
·
Fever
·
Poor skin turgor, dry
skin and dry mouth
·
Sunken fontanels in
children Diagnosis – Stool test
Complications
·
Persistent diarrhea
·
Malnutrition
·
Vitamins and mineral
deficiencies
·
Hypoglycemia resulting
in convulsions and brain damage
·
Electrolyte loss
·
Hypovolemic shock
·
Acute renal failure
Control Measures
·
Promote exclusive
breastfeeding
·
Immunization
·
Using sanitary latrines
·
Keep food and water
clean and closed.
·
Wash hands before eating
and after defaecation.
Treatment
Oral Rehydration Therapy: Give some available liquids like rice
water, oral rehydration solution (ORS) packet to be dissolved in one litre of
drinking water and stir with clean spoon, till it dissolves. Give ¼ to ½ cup
after every loose motion to a child less than 2 years of age and 100-200 ml if
the child is above 2 years. The solution should be consumed within 24 hours and
should not be heated or boiled.
Appropriate feeding
·
Coconut water
·
Rice water
·
Dhal water
·
Smashed banana
·
Watery tea
·
Breakfast feeding to be
continued.
Appropriate drugs:
·
Antibiotics for
Bacterial infection
·
Symptomatic treatment
for fever, vomiting etc.
·
Anti – Motility agents.
·
Intravenous infusion to
severely dehydrated clients.
Related Topics