Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Nervous System
Limbic system and emotions - Brain Functions
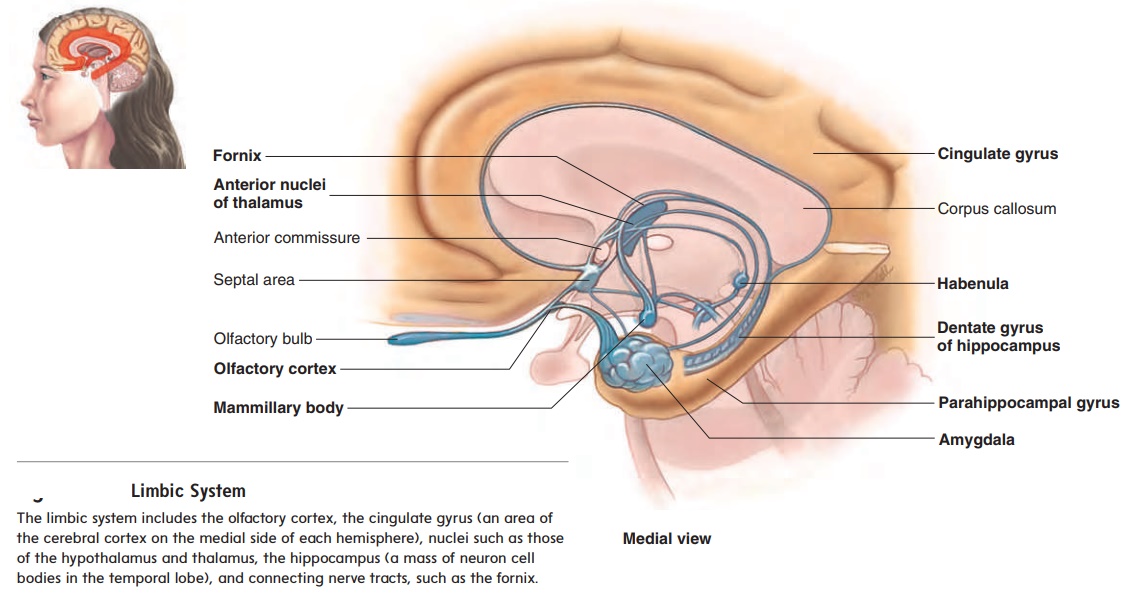
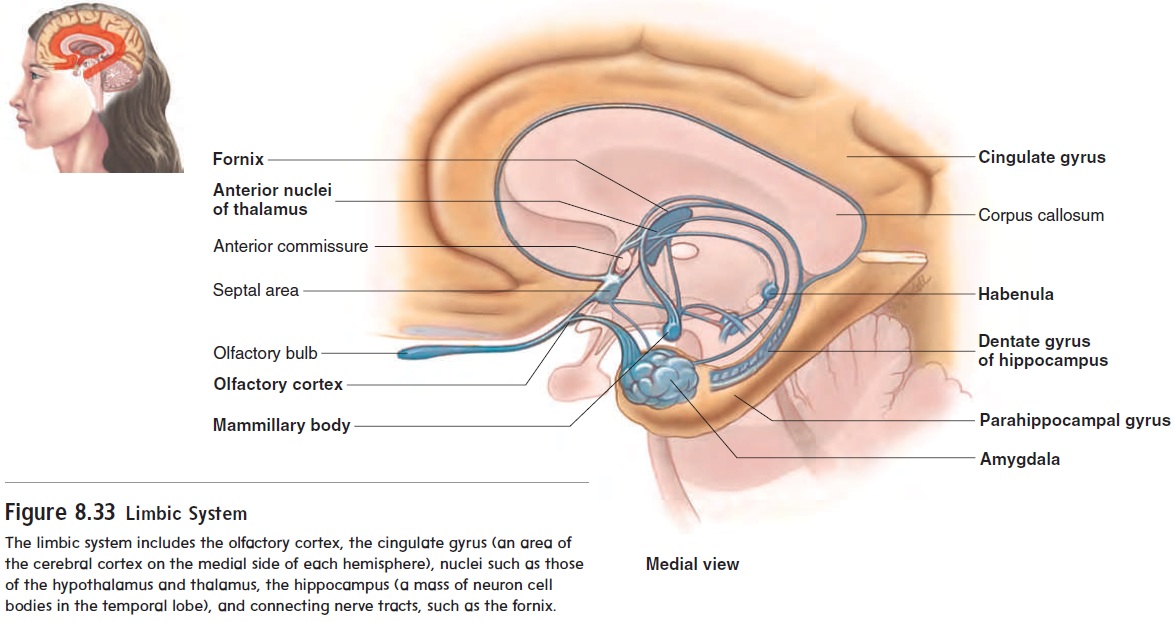
Limbic system and emotions
The olfactory cortex and certain deep cortical regions and nuclei of the cerebrum and the diencephalon are grouped together under the title limbic (lim′ bik; a boundary) system (figure 8.33). The limbic system influences long-term declarative memory, emo-tions, visceral responses to emotions, motivation, and mood. A major source of sensory input to the limbic system is the olfac-tory nerves. The limbic system responds to olfactory stimulation by initiating responses necessary for survival, such as hunger and thirst. The limbic system is connected to, and functionally associated with, the hypothalamus. Lesions in the limbic sys-tem can result in voracious appetite, increased (often perverse) sexual activity, and docility (including loss of normal fear and anger responses).
Related Topics