Chapter: Artificial Intelligence
Learning from observation
LEARNING FROM OBSERVATIONS:
Introduction:
What is learning?
Learning denotes changes in the
system that are adaptive in the sense that they enable the system to do the
same task or tasks drawn from the same population more effectively the next
time (Simon, 1983).
Learning is making useful changes in
our minds (Minsky, 1985).
Learning is constructing or modifying
representations of what is being experienced
(Michalski, 1986).
A computer program learns if it
improves its performance at some task through experience
(Mitchell, 1997).
So what
is learning?
(1)
acquire and organize knowledge (by building,
modifying and organizing internal representations of some external reality);
(2)
discover new knowledge and theories (by creating
hypotheses that explain some data or phenomena);
(3)
acquire skills (by gradually improving their motor
or cognitive skills through repeated practice,
sometimes
involving little or no conscious thought).
(4)
Learning results in changes in the agent (or mind)
that improve its competence and/or efficiency.
(5)
Learning is essential for unknown environments,
(1) i.e., when designer lacks
omniscience
o Learning
is useful as a system construction method,
o Expose
the agent to reality rather than trying to write it down
o
Learning modifies the agent's decision mechanisms
to improve performance
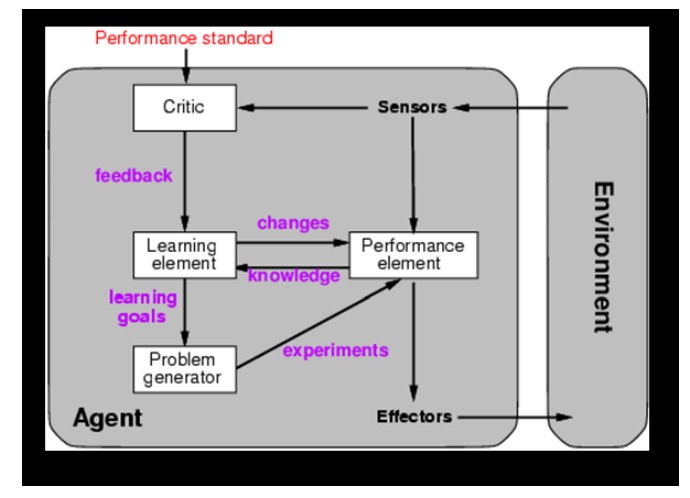
1 FORMS OF LEARNING:
Learning
agents:
• Four
Components
1. Performance Element: collection of
knowledge and procedures to decide on the next action
E.g. walking,
turning, drawing, etc.
2.
Learning Element: takes in feedback from the critic
and modifies the performance element accordingly.
3. Critic:
provides the learning element with information on how well the agent is doing
based on a fixed performance standard. E.g. the audience
Problem
Generator: provides the performance element with suggestions on new actions to
take. Components of the Performance Element
•
A direct mapping from conditions on the current
state to actions
•
Information about the way the world evolves
•
Information about the results of possible actions
the agent can take
•
Utility information indicating the desirability of
world states
Learning element
•
Design of a learning element is affected by
–Which
components of the performance element are to be learned
–What feedback is available to
learn these components
–What
representation is used for the components
Type of
feedback:
–Supervised
learning: correct answers for each example
–Unsupervised
learning: correct answers not given
–Reinforcement
learning: occasional rewards
Related Topics