Chapter: Artificial Intelligence
Importance of Artificial Intelligence(AI)
Importance of AI
Game Playing
You can
buy machines that can play master level chess for a few hundred dollars. There
is some AI in them, but they play well against people mainly through brute
force computation--looking at hundreds of thousands of positions. To beat a
world champion by brute force and known reliable heuristics requires being able
to look at 200 million positions per second.
Speech Recognition
In the
1990s, computer speech recognition reached a practical level for limited
purposes. Thus United Airlines has replaced its keyboard tree for flight
information by a system using speech recognition of flight numbers and city
names. It is quite convenient. On the other hand, while it is possible to
instruct some computers using speech, most users have gone back to the keyboard
and the mouse as still more convenient.
Understanding Natural Language
Just
getting a sequence of words into a computer is not enough. Parsing sentences is
not enough either. The computer has to be provided with an understanding of the
domain the text is about, and this is presently possible only for very limited
domains.
Computer Vision
The world
is composed of three-dimensional objects, but the inputs to the human eye and
computers' TV cameras are two dimensional. Some useful programs can work solely
in two dimensions, but full computer vision requires partial three-dimensional
information that is not just a set of two-dimensional views. At present there
are only limited ways of representing three-dimensional information directly,
and they are not as good as what humans evidently use.
Expert Systems
A
``knowledge engineer'' interviews experts in a certain domain and tries to
embody their knowledge in a computer program for carrying out some task. How
well this works depends on whether the intellectual mechanisms required for the
task are within the present state of AI. When this turned out not to be so,
there were many disappointing results. One of the first expert systems was
MYCIN in 1974, which diagnosed bacterial infections of the blood and suggested
treatments. It did better than medical students or practicing doctors, provided
its limitations were observed. Namely, its ontology included bacteria,
symptoms, and treatments and did not include patients, doctors, hospitals,
death, recovery, and events occurring in time. Its interactions depended on a
single patient being considered. Since the experts consulted by the knowledge
engineers knew about patients, doctors, death, recovery, etc., it is clear that
the knowledge engineers forced what the experts told them into a predetermined
framework. The usefulness of current expert systems depends on their users
having common sense.
Heuristic Classification
One of
the most feasible kinds of expert system given the present knowledge of AI is
to put some information in one of a fixed set of categories using several
sources of information. An example is advising whether to accept a proposed
credit card purchase. Information is available about the owner of the credit
card, his record of payment and also about the item he is buying and about the
establishment from which he is buying it (e.g., about whether there have been
previous credit card frauds at this establishment).
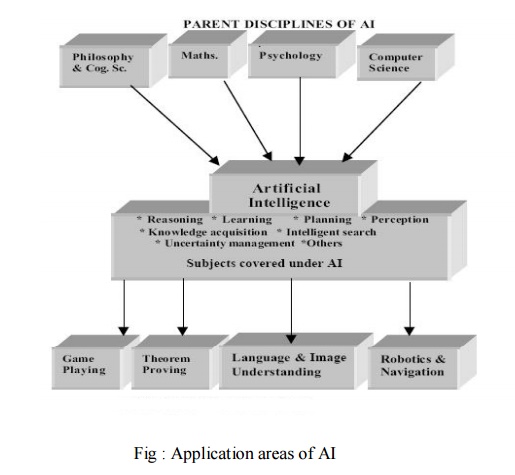
The applications of AI are shown in Fig 1.1:
ĂĽ Consumer Marketing
Have you
ever used any kind of credit/ATM/store card while shopping? o if so, you have very likely been
“input” to an AI algorithm
All of
this information is recorded digitally
Companies
like Nielsen gather this information weekly and search for patterns
general changes in consumer behavior
tracking responses to new products
identifying customer segments: targeted marketing, e.g., they find out
that consumers with sports cars who buy textbooks respond well to offers of new
credit cards.
Algorithms (“data mining”) search data for patterns
based on mathematical theories of learning
Identification
Technologies
ID cards e.g., ATM cards
can be a
nuisance and security risk: cards can be lost, stolen, passwords forgotten, etc
Biometric
Identification, walk up to a locked door
Camera
Fingerprint device
Microphone
Computer uses biometric signature for identification
Face, eyes, fingerprints, voice pattern
This works by comparing data from person at door with stored library
Learning algorithms can learn the matching process by analyzing a large
library database off-line, can improve its performance.
Intrusion
Detection
Computer
security - we each have specific patterns of computer use times of day, lengths
of sessions, command used, sequence of commands, etc
would like to learn the “signature” of each authorized user
can identify non-authorized users
How can the program automatically identify users?
record user’s commands and time intervals
characterize the patterns for each user
model the variability in these patterns
classify (online) any new user by similarity to stored patterns
Machine
Translation
Language problems in international business
e.g., at a meeting of Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese and Swedish
investors, no common language
If you are shipping your software manuals to 127 countries, the solution
is ; hire translators to translate
would be much cheaper if a machine could do this!
How hard
is automated translation
very difficult!
e.g., English to Russian
not only must the words be translated, but their meaning also!
Related Topics