Chapter: Biochemistry: Biochemistry and the Organization of Cells
How is prokaryotic DNA organized without a nucleus?
Prokaryotic Cells
Although
no well-defined nucleus is present in prokaryotes, the DNA of the cell is
concentrated in one region called the nuclear
region. This part of the cell directs the workings of the cell, much as the
eukaryotic nucleus does.
How is prokaryotic DNA organized without a nucleus?
The DNA
of prokaryotes is not complexed with proteins in extensive arrays with
specified architecture, as is the DNA of eukaryotes. In general, there is only
a single, closed, circular molecule of DNA in prokaryotes. This circle of DNA,
which is the genome, is attached to the cell membrane. Before a pro-karyotic
cell divides, the DNA replicates itself, and both DNA circles are bound to the
plasma membrane. The cell then divides, and each of the two daughter cells
receives one copy of the DNA (Figure 1.10).
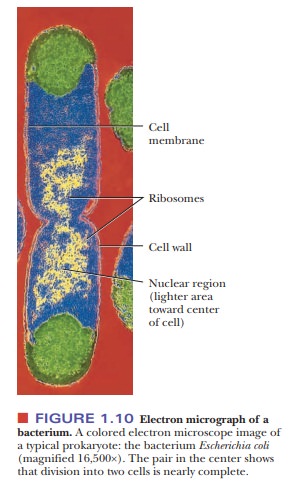
In a
prokaryotic cell, the cytosol (the fluid portion of the cell outside the
nuclear region) frequently has a slightly granular appearance because of the
presence of ribosomes. Because these
consist of RNA and protein, they are also called ribonucleoprotein particles; they are the sites of protein
synthesis in all organisms. The presence of ribosomes is the main visible
feature of prokaryotic cytosol. (Membrane-bound organelles, characteristic of
eukaryotes, are not found in prokaryotes.)
Every
cell is separated from the outside world by a cell membrane, or plasma membrane, an assemblage of lipid molecules
and proteins. In addition to the cell membrane and external to it, a
prokaryotic bacterial cell has a cellwall,
which is made up mostly of polysaccharide material, a feature it shareswith
eukaryotic plant cells. The chemical natures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
walls differ somewhat, but a common feature is that the polymerization of
sugars produces the polysaccharides found in both. Because the cell wall is
made up of rigid material, it presumably serves as protection for the cell.
Summary
Prokaryotes
have a nuclear region, which contains DNA, and ribosomes, the site of protein
synthesis, as their main features. They have a cell mem-brane, but do not have
an internal membrane system.
Related Topics