Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipid Metabolism
Fatty acids
Fatty
acids
The fatty acids are the basic units of lipid
molecules. Fatty acids are derivatives of aliphatic hydrocarbon chain that
contains a carboxylic acid group. Over 200 fatty acids have been isolated from
various lipids. They differ among themselves in hydrocarbon chain length,
number and position of double bonds as well as in the nature of substituents
such as oxy-, keto-, epoxy groups and cyclic structure. Depending on the
absence, or presence of double bonds, they are classified into saturated and
unsaturated fatty acids.
Saturated fatty acids, do not contain double
bonds. The hydrocarbon chain may contain 12 to 18 carbon atoms. eg. palmitic
and stearic acids
CH3 (CH2)14 COOH - Palmitic acid (C-16)
CH3 (CH2)16 COOH -
Stearic acid (C-18)
Unsaturated fatty acids are classified into different types depending on the number of double bonds present in the hydrocarbon chain. These fatty acids are mainly found in plant lipids.
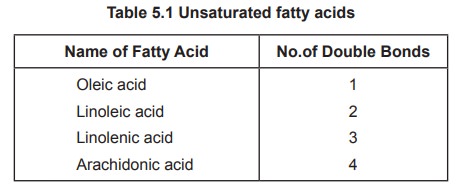
Name of Fatty Acid No.of Double Bonds
Oleic acid
1
Linoleic acid 2
Linolenic acid
3
Arachidonic acid
4
Essential fatty acids
Fatty acids required in the diet are called
essential fatty acids (EFA). They are not synthesized by the body and are
mainly polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
eg. Linoleic
acid
Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Functions of essential fatty acids
They are required for membrane structure and
function, transport of cholesterol, formation of lipoproteins and prevention of
fatty liver.
Deficiency of essential fatty acids
The deficiency of essential fatty acid results
in phrynoderma or toad skin.
Related Topics