Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipid Metabolism
Biosynthesis of fatty acids
Biosynthesis of fatty acids
1.
Biosynthesis
of fatty acids occurs in all organisms and in mammals it occurs mainly in
adipose tissue, mammary glands, and liver.
2.
Fatty
acid synthesis takes place in the cytosol in two steps.
·
Formation
of medium chain fatty acid of chain length 16 carbon atoms.
·
Lengthening
of this carbon chain in microsomes for larger fatty acids.
3.
Acetyl
CoA serves as a source of carbon atoms for saturated as well as unsaturated
fatty acids. Acetyl CoA can be formed from excessive dietary glucose and
glucogenic amino acids (amino acids which can be converted to glucose).
Carbohydrates and aminoacids in the presence of oxygen is converted to pyruvate
which inturn can be converted to acetyl CoA
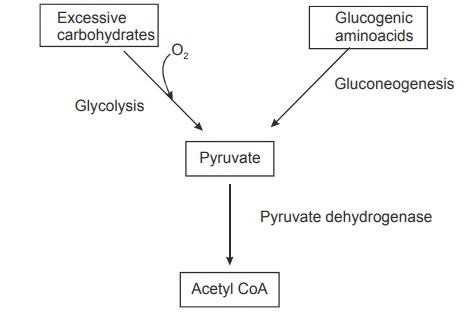
The synthesis of fatty acid from acetyl CoA
takes place with aid of a multi-enzyme complex termed as fatty acid synthetase
complex. Palmitic acid is the major product of the fatty acids synthetase
complex mediated reaction and hence it is also called as palmitate synthetase.
It is a dimer with two identical subunits namely subunit-1 and subunit-2
arranged in a head to tail fashion. Each monomer of this enzyme complex
contains seven enzymes; of these, each is assigned a definite function.
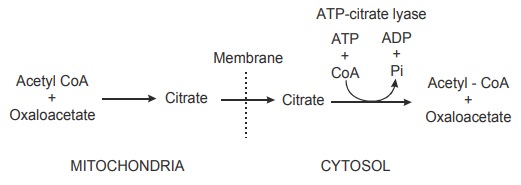
Migration of Acetyl CoA for the bio synthesis of Fatty acids
Formation of acetyl CoA from pyruvate takes
place in mitochondria. Mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to acetyl CoA.
Migration of acetyl CoA from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm is facilitated
by the condensation of the acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate to form citrate which
is permeable to mitochondrial membrane. In the cytoplasm, citrate readily
decomposed back to acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate in the presence of ATP and
co-enzyme A by the action of an enzyme called ATP - Citrate lyase.
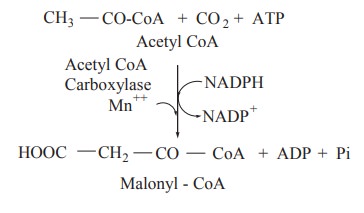
Conversion of Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA
The acetyl - CoA is carboxylated in the
cytoplasm in the presence of acetyl CoA carboxylase, a vitamin Biotin
containing enzyme, which helps in carbondioxide fixation. Acetyl CoA
carboxylase is the regulatory enzyme in the fatty acid biosynthesis.
Conversion of malonyl CoA to palmitic acid
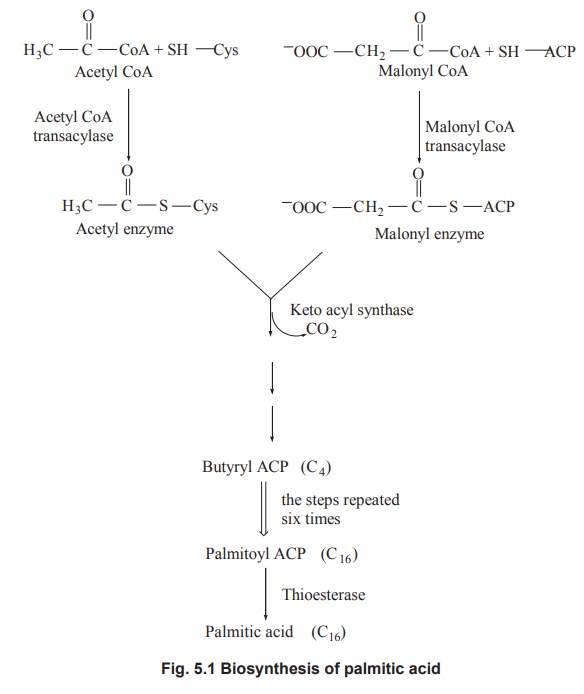
The malonyl CoA is converted to palmitic acid by
several steps and each of these steps are catalysed by different enzymes of
fatty acid synthetase complex.
Acetyl CoA and malonyl CoA condenses to form
butyryl-ACP with the formation of intermediates. This cycle repeats itself six
times and in each cycle two carbon atoms (malonyl CoA) is added to butyryl ACP,
ultimately resulting in the formation of palmitoyl CoA, a 16 carbon molecule.
Related Topics