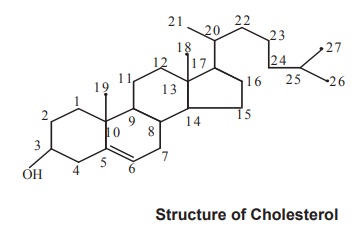
Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipid Metabolism
Biosynthesis of cholesterol
Biosynthesis of cholesterol
Important intermediates of cholesterol
Biosynthesis and enzymes involved.
1. Formation of acetyl CoA
A molecule of acetic acid combines with coenzyme
A (CoA) to produce Acetyl CoA in the presence of an enzyme Acetyl CoA
synthetase.
2. Formation of acetoacetyl CoA
Two molecules of acetyl-CoA condense to form an
acetoacetyl-CoA molecule, catalyzed by the enzyme “thiolase”.
3. Formation of HMG CoA
The acetoacetyl-CoA further undergoes
condensation with one more molecule of acetyl-CoA to form HMG-CoA (3-Hydroxy
3-Methyl Glutaryl-CoA). The enzyme which mediates this reaction is called
HMG-CoA synthetase.
4. Formation of mevalonate
The HMG-CoA is reduced to form mevalonate by
NADPH + H+ dependent reductase (HMG-CoA reductase). This is the rate limiting
enzyme in the pathway of cholesterol biosynthesis.
5. Mevalonate thus formed is then converted to
squalene through various steps.
6. Squalene, with the formation of various
intermediates finally give rise to the end product cholesterol.
Related Topics