Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : The Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors
Contraception with Progestins Alone - Hormonal Contraception
Contraception with Progestins
Alone
Small doses of
progestins administered orally or by implantation under the skin can be used
for contraception. They are particularly suited for use in patients for whom
estrogen administration is undesirable. They are about as effective as
intrauterine devices or combination pills containing 20–30 mcg of ethinyl
estradiol. There is a high incidence of abnormal bleeding.
Effective
contraception can also be achieved by injecting 150 mg of depot
medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) every 3 months. After a 150 mg dose,
ovulation is inhibited for at least 14 weeks. Almost all users experience episodes
of unpredictable spotting and bleeding, particularly during the first year of
use. Spotting and bleeding decrease with time, and amenorrhea is common. This
preparation is not desirable for women planning a pregnancy soon after
cessation of therapy because ovulation sup-pression can sometimes persist for
as long as 18 months after the last injection. Long-term DMPA use reduces
menstrual blood loss and is associated with a decreased risk of endometrial
cancer. Suppression of endogenous estrogen secretion may be associated with a
reversible reduction in bone density, and changes in plasma lipids are
associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
The progestin implant
method utilizes the subcutaneous implantation of capsules containing
etonogestrel. These capsules release one fifth to one third as much steroid as
oral agents, are extremely effective, and last for 2–4 years. The low levels of
hor-mone have little effect on lipoprotein and carbohydrate metabo-lism or
blood pressure. The disadvantages include the need for surgical insertion and
removal of capsules and some irregular bleeding rather than predictable menses.
An association of intra-cranial hypertension with an earlier type of implant
utilizing norgestrel was observed in a small number of women. Patients
experiencing headache or visual disturbances should be checked for papilledema.
Contraception with progestins is useful in patients with hepatic disease, hypertension, psychosis or mental retardation, or prior thromboembolism. The side effects include headache, dizziness, bloating and weight gain of 1–2 kg, and a reversible reduction of glucose tolerance.
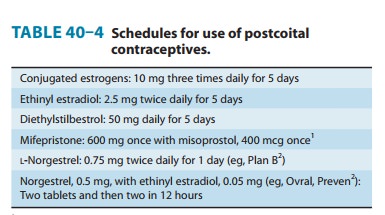
Postcoital Contraceptives
Pregnancy
can be prevented following coitus by the administration of estrogens alone,
progestin alone, or in combination (“morningafter”
contraception). When treatment is begun within 72 hours,it is effective 99%
of the time. Some effective schedules are shown in Table 40–4. The hormones are
often administered with antie-metics, since 40% of patients have nausea or
vomiting. Other adverse effects include headache, dizziness, breast tenderness,
and abdominal and leg cramps.
Mifepristone,
an antagonist at progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors, has a luteolytic
effect and is effective as a postcoital contraceptive. When combined with a
prostaglandin it is also an effective abortifacient.
Beneficial Effects of Oral Contraceptives
It has become apparent
that reduction in the dose of the constitu-ents of oral contraceptives has
markedly reduced mild and severe adverse effects, providing a relatively safe
and convenient method of contraception for many young women. Treatment with
oral contraceptives has also been shown to be associated with many benefits
unrelated to contraception. These include a reduced risk of ovarian cysts,
ovarian and endometrial cancer, and benign breast disease. There is a lower
incidence of ectopic pregnancy. Iron deficiency and rheumatoid arthritis are
less common, and premenstrual symptoms, dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, acne, and
hirsutism may be ameliorated with their use.
Related Topics