Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : The Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors
Clinical Uses - Hormonal Contraception
Clinical Uses
The
most important use of combined estrogens and progestins is for oral
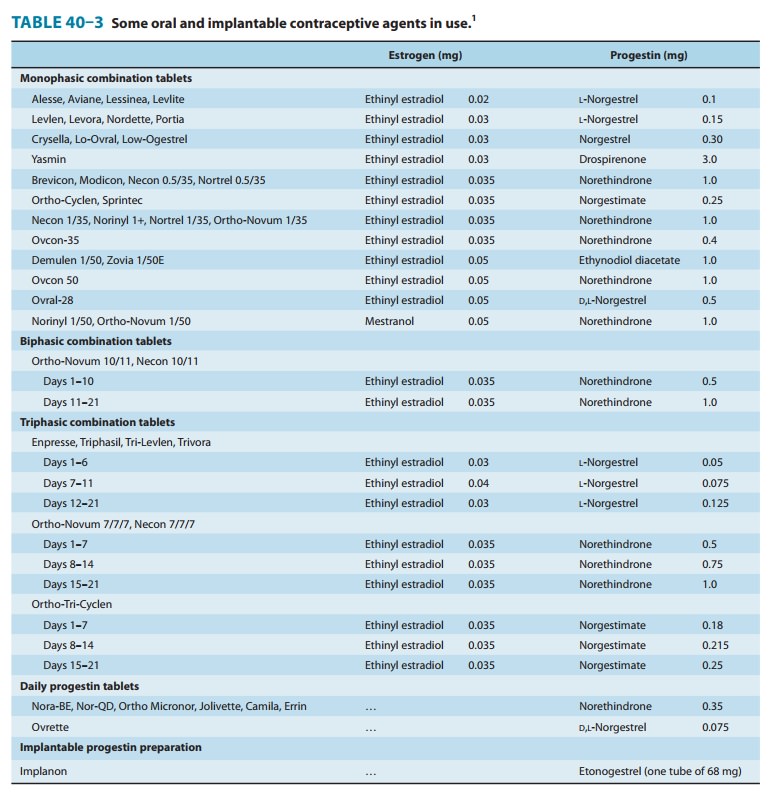
contraception. A large number of preparations are available for this specific purpose, some of
which are listed in Table 40–3. They are specially packaged for ease of
administra-tion. In general, they are very effective; when these agents are
taken according to directions, the risk of conception is extremely small. The
pregnancy rate with combination agents is estimated to be about 0.5–1 per 100
woman years at risk. Contraceptive failure has been observed in some patients
when one or more doses are missed, if phenytoin is also being used (which may
increase catabolism of the compounds), or if antibiotics are taken that alter
enterohepatic cycling of metabolites.
Progestins
and estrogens are also useful in the treatment of endometriosis. When severe
dysmenorrhea is the major symptom, the suppression of ovulation with estrogen
alone may be followed by painless periods. However, in most patients this
approach to therapy is inadequate. The long-term administration of large doses
of progestins or combinations of progestins and estrogens prevents the periodic
breakdown of the endometrial tissue and in some cases will lead to endometrial
fibrosis and prevent the reactivation of implants for prolonged periods.
As
is true with most hormonal preparations, many of the unde-sired effects are
physiologic or pharmacologic actions that are objec-tionable only because they
are not pertinent to the situation for which they are being used. Therefore,
the product containing the smallest effective amounts of hormones should be
selected for use.
Related Topics